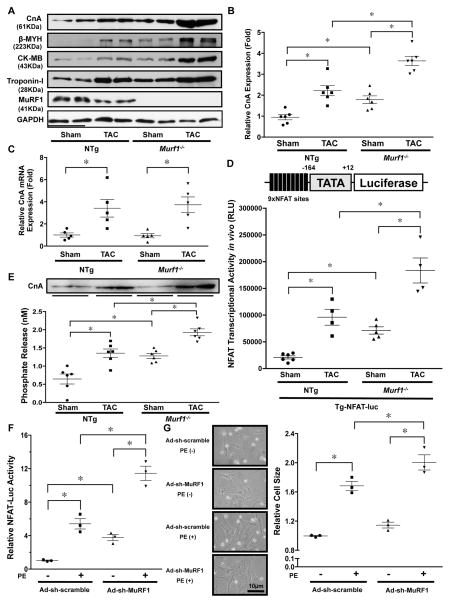
Figure 3. MuRF1 negatively regulates the calcineurin-NFAT pathway.
A, The protein levels of CnA, β-MYH, CK-MB, and Troponin-I at baseline and in response to TAC (4 weeks) in Murf1−/− and NTg mice. B, The results of the quantitative analysis of the CnA protein level shown in Figure 3A. * P<0.05 (N=6). C, mRNA expression of the CnA gene was measured by quantitative RT-PCR. * p<0.05 (N=5). D, Murf1−/− enhances NFAT activity at baseline and in response to TAC. Tg-NFAT-Luc mice were crossed with Murf1−/− or control mice, and each mouse group was subjected to either sham or TAC operation. After one week, NFAT-Luc activity in the heart homogenates was evaluated. * P<0.05 (N=4–6). E, Calcineurin phosphatase activity in the hearts of Murf1−/− or NTg mice subjected to either sham or TAC operation. * P<0.05 (N=6). Upper panel shows an immunoblot of the relative amounts of CnA protein in the homogenates being assessed in these experiments. F, MuRF1 inhibits phenylephrine (PE)-induced cardiac hypertrophy and NFAT activation. Cardiomyocytes were transduced with Ad-sh-MuRF1 and transfected with NFAT-luciferase reporter vector. * P<0.05 (N=3). G, Left: Representative images of neonatal rat cultured cardiomyocytes treated with PE and the indicated adenoviruses. Right: Relative cell size of myocytes treated with the indicated adenoviruses in the presence or absence of PE for 72 hours was examined. * P<0.05 (N=3).