Figure 2.
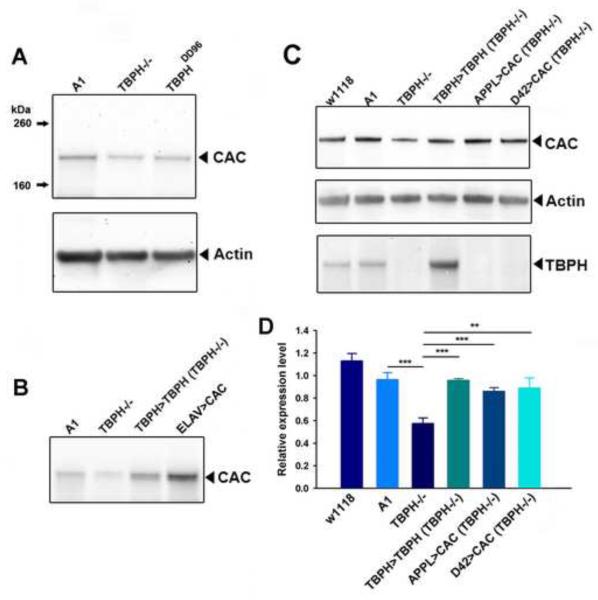
The levels of cacophony are reduced in TBPH null mutants. A. Representative immunoblot from 3rd instar larvae showing the protein levels of cacophony (CAC) and actin as a loading control. The levels of cacophony were reduced in TBPH null mutants (TBPH −/−) compared to the A1 control line (line generated by precise excision of transposon – see Hazelett et al, 2012). Cacophony is also reduced in another independently generated TBPH mutant line, TBPHDD96 (Diaper et al, 2013). B. Cacophony levels were restored in TBPH rescue (TBPH>TBPH) lines and enhanced when cacophony was expressed under the control of a pan-neuronal driver (ELAV>CAC). C. Cacophony levels were also restored when cacophony was expressed either in all neurons (APPL>CAC) or only in motor neurons (D42>CAC). This blot was also re-probed for TBPH. D. Quantification of immunoblots. The intensity of the cacophony immunoreactive band was quantified, normalized to the intensity of the actin band and compared to the ratio obtained for the A1 control. ANOVA analysis shows that the relative expression of cacophony in TBPH mutants is significantly reduced (** p<0.01, *** p<0.001, n=6) compared to all other genotypes.