FIGURE 1.
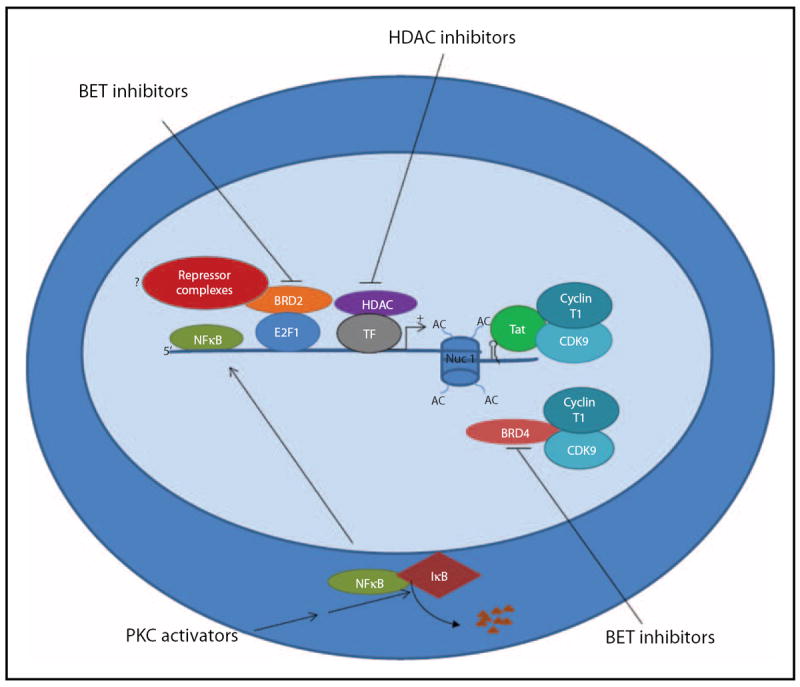
HIV induction by PKC activators and HDAC and BET inhibitors: NFκB is sequestered in the cytoplasm by IκB. PKC activators such as Prostratin and Bryostatin induce HIV from latency through activation of the PKC/NFκB signaling pathway leading to degradation of IκB and translocation of NFκB to the nucleus where it binds to NFκB biding sites at the HIV LTR and activates transcription. HDACs are recruited to the HIV LTR by several different transcription factor complexes (designated here as TF for simplicity) and promote transcriptional repression of the HIV LTR in part by removing acetyl groups from the lysine tails of histones associated with the nucleosome bound provirus, thus increasing the tight interaction of histones with proviral DNA and thereby creating an environment less conducive for transcription. Inhibition of HDAC activities by compounds such as Vorinostat and Panobinostat lead to acetylation (AC) of lysine residues on histones tails resulting in a relaxation of the interaction of histones and DNA, facilitating the binding of positive transcription factors that induce HIV transcription initiation and elongation. Finally, inhibition of BET protein family members BRD2 and BRD4 by BET inhibitors such as JQ1 leads to HIV promoter activation through separate modes of action. BRD4 competes with Tat for the binding of PTEF-b (composed of CDK9 and cyclin T1). Inhibition of BRD4 allows enhanced Tat binding to PTEF-b and transactivation that is required for productive transcription elongation. Although less clear, it is hypothesized that inhibition of BRD2 may block recruitment of repressive transcription complexes (in exchange for activator complexes), thus promoting HIV transcription. BET, bromodomain extraterminal; BRD, bromodomain containing; HDAC, histone deacetylase; LTR, long terminal repeat; PKC, protein kinase C; PTEF-b, positive transcription elongation factor b.
