Fig. 4.
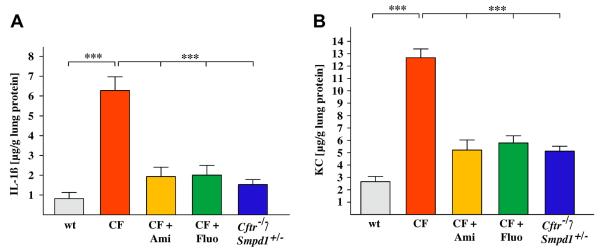
Long-term treatment with functional acid sphingomyelinase inhibitors or genetic heterozygosity protects cystic fibrosis mice from lung inflammation. Concentrations of IL-1 and KC are elevated in lungs of untreated, 8 month-old Cftr-deficient mice. Levels of these inflammatory markers are corrected by long-term treatment with amitriptyline or fluoxetine or heterozygosity of acid sphingomyelinase. IL-1 and KC levels were measured in lung homogenates by ELISA. Displayed is the mean ± SD from each 5 mice, ***p < 0.001 compared as indicated.
