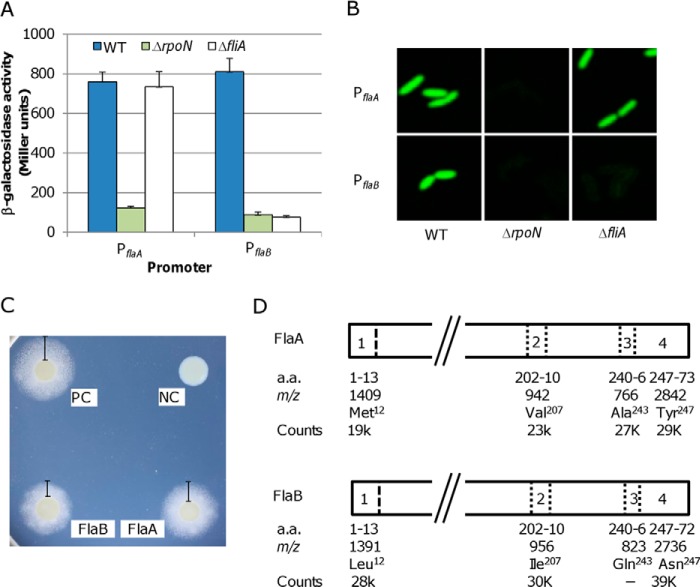
FIGURE 2.
Expression, secretion, and assembly into filaments of FlaA and FlaB. A, promoter activities of the flaA and flaB genes were determined by measuring β-galactosidase levels using PflaA-lacZ and PflaB-lacZ reporter constructs in the wild type (WT), ΔrpoN, and ΔfliA strains. Whole-cell lysates were prepared from S. oneidensis cultures in mid-exponential growth phase and assayed. Quantification of the promoter activities was normalized to the total protein in each strain. The values are the mean ± S.D. (error bars) (n = 5). B, promoter activities were monitored using PflaA-gfp and PflaB-gfp reporter constructs in the wild type (WT), ΔrpoN, and ΔfliA strains. Experiments were repeated three times, and similar results were obtained. C, YplA secretion assay. Flagellin-YplA fusion proteins were composed of the N-terminal 36 residues of either flagellin and Y. enterocolitica YplA lacking its native T3S signal. Positive control (PC) was the Y. enterocolitica wild type strain JB580v, and negative control (NC) was the Y. enterocolitica ΔyplAB strain harboring the pCSP50 vector. The experiments were performed three times, and similar results were obtained. D, abundance of the signature peptides identified by LC-MS/MS analysis of tryptic digests of flagellins from the wild type filament. The approximate m/z values of these tryptic peptides were given according to our previous study (28). The third peptide of FlaB was missed in the analysis. Signal intensities by counts were used to calculate the abundance of FlaA and FlaB in the wild type filament.