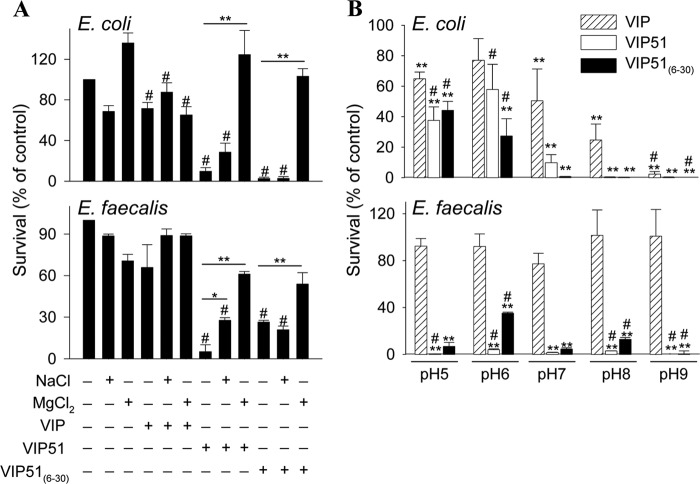
FIGURE 3.
Determinants influencing the antibacterial effect of the VIP derivatives. A, effect of the ionic strength of the medium on the activity of native VIP and the VIP derivatives against E. coli and E. faecalis. Bacteria were incubated with VIP, VIP51, and VIP51(6–30) (each at 5 μm) in the absence or presence of 180 mm NaCl or 50 mm MgCl2 for 3 h. *, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.001 versus peptide-treated bacteria; #, p < 0.05 versus untreated bacteria at each condition. B, effect of pH of the medium on the antimicrobial activity of VIP and the VIP derivatives (5 μm, 3 h of culture) against E. coli and E. faecalis.**, p < 0.001 versus controls at each pH; #, p < 0.05 versus peptide-treated bacteria at pH 7.0. In both panels, survival was determined as described in the legend to Fig. 1. The mean ± S.E. (error bars) (n = 3, each performed in duplicate) is shown.