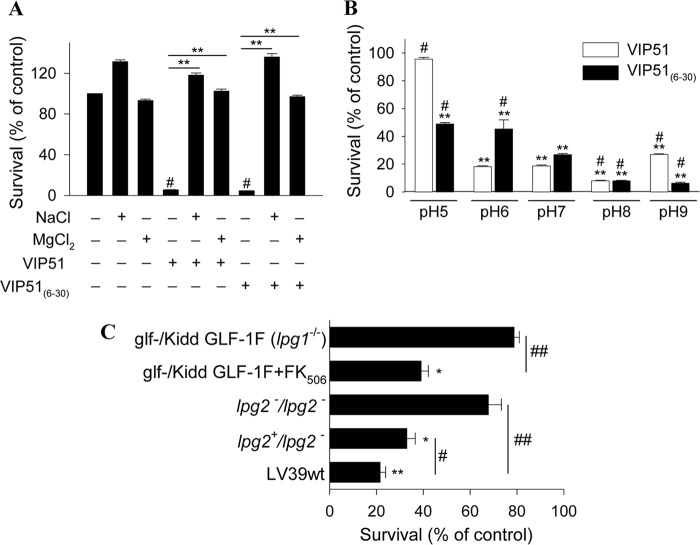
FIGURE 8.
Determinants influencing leishmanicidal activity of the VIP derivatives. A, effect of the ionic strength of the medium on the activity of VIP analogues against L. major. Survival of parasites incubated with VIP51 and VIP51(6–30) (12 μm) in the absence or presence of 180 mm NaCl or 50 mm MgCl2 for 4 h. **, p < 0.001. B, effect of pH of the medium on the antiparasitic effect of the VIP derivatives (12 μm, 4 h of culture) against L. major. **, p < 0.001 versus controls at each pH; #, p < 0.05 versus peptide-treated parasites at pH 7.0. C, VIP51 requires the interaction with LPG and PG of the parasite surface to kill L. major promastigotes. The effect of VIP51 on the cell viability of the mutant strain of L. major glf−/Kidd GLF-1F lacking LPG (glf−/Kidd GLF-1F L. major Friedlin V1 parasites treated with FK506 that induces LPG expression were used as the WT strain for comparison) or the L. major lpg2−/− and lpg2+/− mutants lacking PG (LV39wt was used as the WT strain for comparison) is shown. Survival was expressed as a percentage of cell viability of their corresponding WT strains. Data are the mean ± S.E. (error bars) of three independent experiments, each performed in duplicate. *, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.001 versus untreated parasites; #, p < 0.01; ##, p < 0.001 versus WT treated parasites.