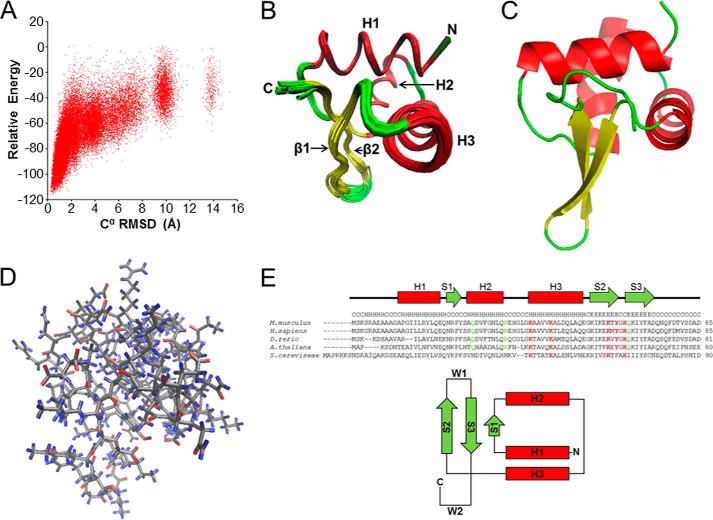
FIGURE 2.
NMR structure of 1–84HOP2. A, NMR structure determination of 1–84HOP2. Shown is a plot of chemical shift-rescored ROSETTA all-atom energy versus Cα r.m.s.d. from the lowest energy structure showing convergence of structure calculation. B, diagram of superimposed 20 refined low-energy structures. C, carboxyl-terminal; N, amino-terminal; H, helix; β, beta. Secondary structures are colored as follows: red, helices, yellow, β-sheets, and green, loops. C, schematic diagram of the lowest energy structure. Secondary structures are colored as described in B. D, backbone atom representation of 1–84HOP2. Gray, carbon, nitrogen, and sulfur; blue, hydrogen; and red, oxygen. E, alignment of the HOP2 amino-terminal primary sequence and topology of a typical winged helix fold. Highlighted are conserved (red) and partially conserved (green) amino acids. The secondary structure prediction for the mouse sequence was obtained using the nnpredict program; H, α-helix. S represents β-strands, and W1 and W2 are loops or wings. M. musculus, Mus musculus; H. sapiens, Homo sapiens; D. rerio, Danio rerio; A. thaliana, Arabidopsis thaliana; S. cereviseae, Saccharomyces cereviseae.