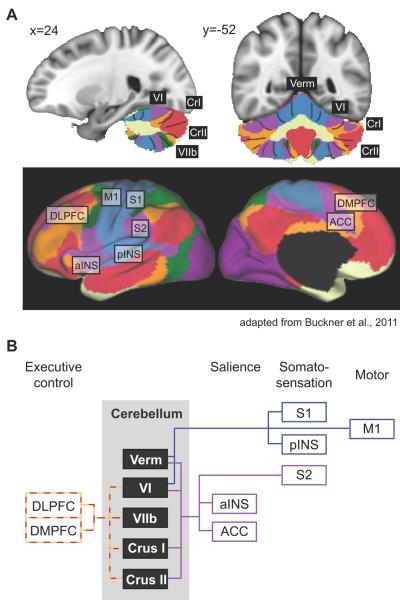
Figure 2. Cerebellar functional connectivity to cerebral resting state networks.
A) Colors in the cerebellum correspond to areas functionally correlated to cerebral resting state networks. Coordinates correspond to MNI atlas space. Figure adapted from Buckner et al., 2011. B) Schematic of cerebral connectivity in cerebellar areas with gray matter deficits in addiction, and fMRI activation in response to acute drug exposure and drug craving. Colored lines correspond to the colored resting state networks in panel A. Each cerebral area is classified based on its contribution to different functional processes (i.e. cognitive control, salience, etc.). ACC, anterior cingulate cortex; aINS, anterior insula; DLPFC, dorsolateral prefrontal cortex; DMPFC, dorsomedial prefrontal cortex; M1, primary motor cortex; pINS, posterior insula; S1, primary somatosensory cortex; S2, secondary somatosensory cortex.