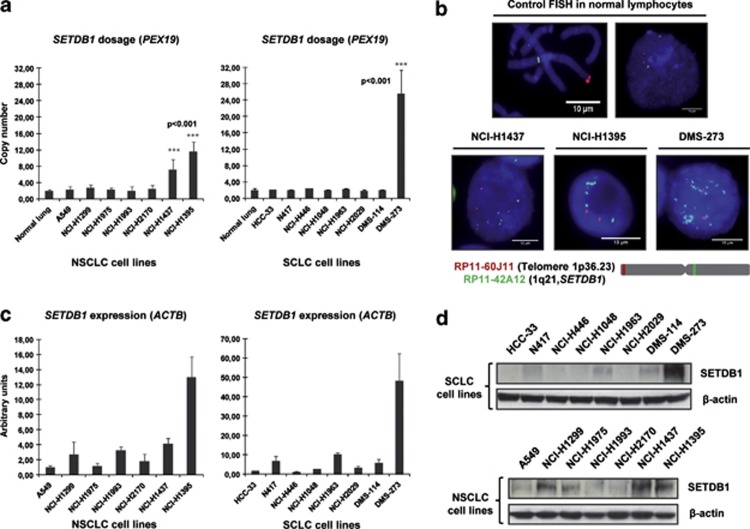
Figure 1.
Determination of SETDB1 gene amplification and its association with RNA and protein overexpression in lung cancer cell lines. (a) Assessment of SETDB1 copy-number by quantitative genomic PCR. Amplification frequency of SETDB1 (evaluated with SYBR Green, Bio-Rad, Hercules, CA, USA) was calculated by the standard curve method using the 7900HT SDS program. To define an internal control gene, we chose chromosome 1p36.23 because it is the least aneuploid region among our cell lines (PEX19 gene). Primers are available upon request. DNA from normal lung was used as the reference standard. Results are reported as n-fold copy-number increase relative to the PEX19 gene. (b) Fluorescence in situ hybridization for the SETDB1 gene. The UCSC genome browser (http://www.genome.ucsc.edu) was used to select the bacterial artificial chromosome (BAC) clone spanning the 1q21 region for the SETDB1 gene: RP11-42A12. A telomeric BAC clone located in the telomeric 1p36.23 region was used as a control. The BACs were obtained from the BACPAC Resource Center at the Children's Hospital Oakland Research Institute (Oakland, CA, USA). SETDB1 and telomeric probes were labeled with Spectrum Green and Red dUTP (Abbott, Wiesbaden, Germany), respectively, using a CGH Nick Translation Reagent Kit (Abbott Molecular Inc., Des Plaines, IL, USA). The samples were counterstained with 4',6-diamidino-2-phenylindole in Vectashield antifade solution (Burlingame, CA, USA). Gene amplification was observed in the interphases of NCI-H1437, NCI-H1395 and DMS-273. Probes were verified to give a single signal on normal commercial lymphocyte metaphase slides (CGH Reagents, Abbott). Quantitative reverse transcription–PCR (c) and western blot (d) demonstrate higher levels of SETDB1 mRNA and protein (ab12317, Abcam, Cambridge, UK), respectively, in amplified cancer cell lines (H1437, NCI-H1395 and DMS-273) than that in unamplified cells. PCR primers are available upon request.