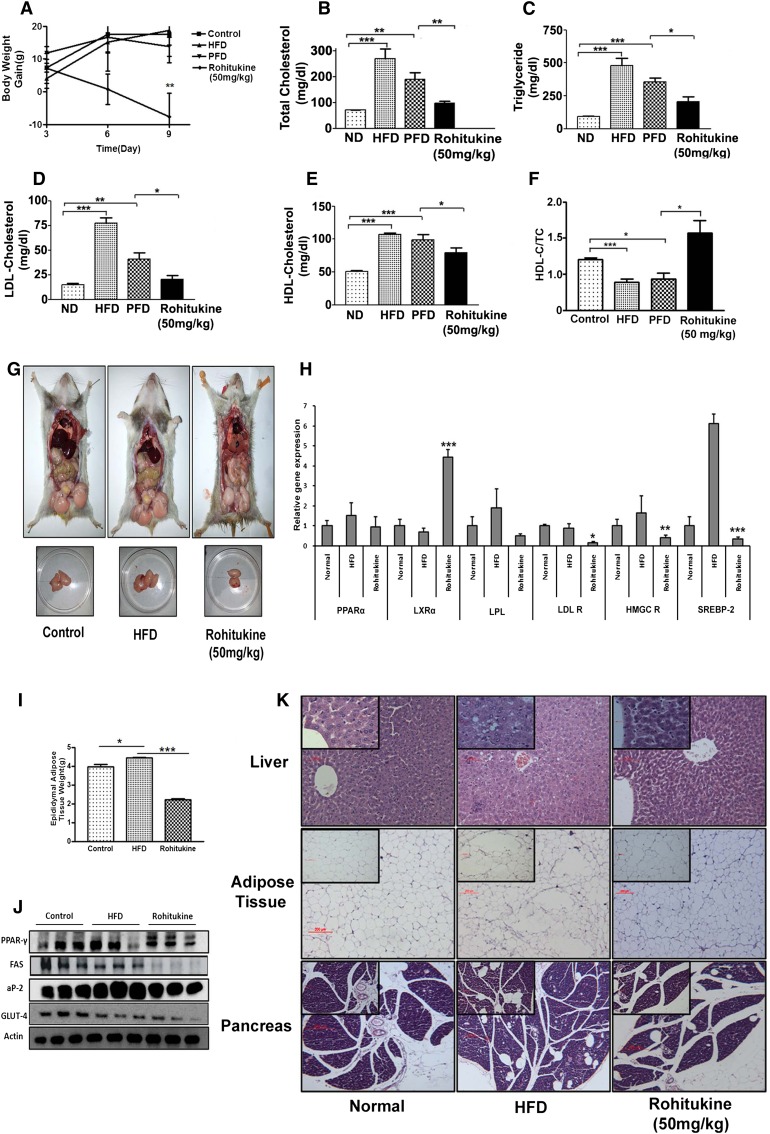
Fig. 5.
Effect of rohitukine administration on normal chow diet (ND)-, HFD-, and PFD-fed dyslipidemic Syrian golden hamsters. A: Mean body weight gain of different groups showed that rohitukine significantly decreased body weight gain by the end of the experiment. Rohitukine showed significantly decreased TC (B), total TG (C), LDL-c (D), and HDL-c (E) compared with PFD. F: Rohitukine significantly increased the HDL-c/TC ratio. G: Rohitukine reduced gonadal fat mass as compared with the HFD-fed group. H: Hepatic mRNA expression levels in HFD-fed and HFD+rohitukine-fed (50 mg/kg) groups were analyzed at the end of the experiment. LXRα expression was increased significantly to 4-fold, while significant reduction was observed in LDL R, HMGC R, and SREBP-2 in the HFD+rohitukine-fed group. I: Significantly increased epididymal fat weight in the HFD-fed group is reduced significantly in the rohitukine-fed animal group. J: Protein level expression of PPARγ, FAS, aP2, and GLUT-4 in epididymal fat tissue in control, HFD-fed, and HFD+rohitukine-fed groups. K: HE staining of liver, adipose, and pancreas tissues. Images in the insets are magnified images from the same section. Rohitukine decreased the lipid accumulation in liver compared with HFD-fed animals. Each bar represents mean ± SEM, with significance expressed as *** P < 0.0001, ** P < 0.001, * P < 0.05.