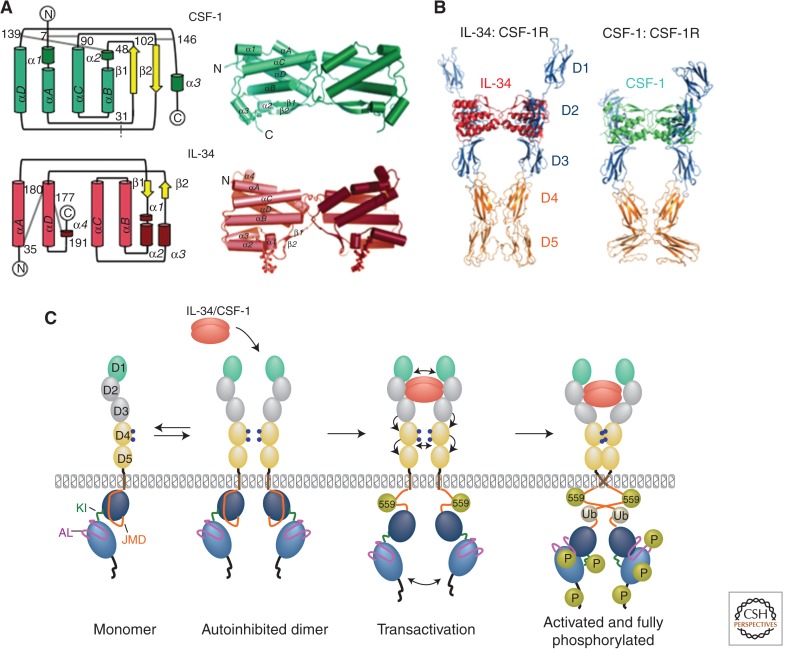
Figure 2.
Structure of CSF-1, IL-34, and CSF-1R ligand–receptor complexes. (A) Topological diagrams of monomeric (left) and ribbon representations of dimeric CSF-1 (top) and IL-34 (bottom) (based on data from Pandit et al. 1992; Liu et al. 2012; Ma et al. 2012). Gray lines in topological diagrams represent intramolecular disulfide bridges; dotted gray line in CSF-1 indicates position of the intermolecular disulfide bond. (B) Structure of CSF-1R ectodomain complex with IL-34 and CSF-1 (based on data from Felix et al. 2013). (C) Model of early events in CSF-1R activation (based on data from Verstraete and Savvides 2012). Gold spheres, phosphotyrosines (P), gray spheres, ubiquitination (Ub). Note that phosphorylation of CSF-1R tyrosine residue 559 and intracellular domain ubiquitination are important for full receptor activation and tyrosine phosphorylation.