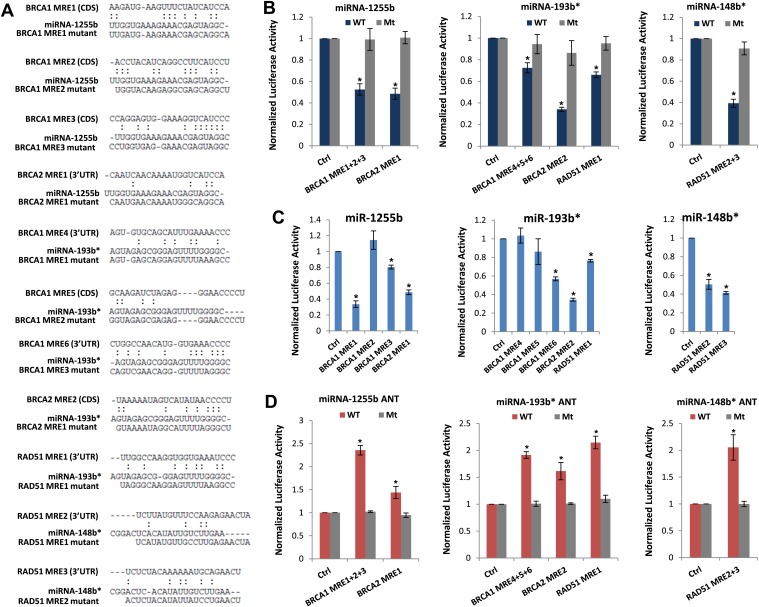
Figure 4. Predicted miRNA recognition sites (MREs) of miRNAs and their impact on targets.
(A) Predicted MREs were obtained from PITA (http://genie.weizmann.ac.il/pubs/mir07/mir07_prediction.html) and their mutants were generated by mutating nucleotides providing complementarity and G-U wobble to corresponding miRNAs. The region where MRE is located in the gene is indicated in the parentheses. CDS: coding sequence, 3′UTR: 3′ untraslated region. (B) Luciferase reporter assay to assess direct interaction of miR-1255b, miR-193b*, and miR-148b* with BRCA1, BRCA2, and RAD51. Combinations of predicted miRNA recognition sites (MREs) for each putative target transcript of miR-1255b, miR-193b*, and miR-148b* were cloned into the luciferase reporter vector and transfected in MDA-MB231 cells along with the indicated miRNA mimics. Renilla luciferase activity of the reporter was measured 48 hr after transfection by normalization to an internal firefly luciferase control. Mean ± SD of three independent experiments is shown and statistical significance is indicated by * (p<0.05). (C) Luciferase reporter assay for individual MREs for each target of miRNAs was performed in the same way as described in Figure 4B. Mean ± SD of three independent experiments is shown and statistical significance is indicated by *(p<0.05). (D) Luciferase reporter assay with miR-1255b, miR-193b*, and miR-148b* ANTs. Combinations of predicted miRNA recognition sites (MREs) in the luciferase vector for each putative target transcript of miR-1255b, miR-193b*, and miR-148b* were transfected in MDA-MB231 cells along with the indicated miRNA ANTs. Renilla luciferase activity of the reporter was measured 48 hr after transfection by normalization to an internal firefly luciferase control. Mean ± SD of three independent experiments is shown and statistical significance is indicated by *(p<0.05).