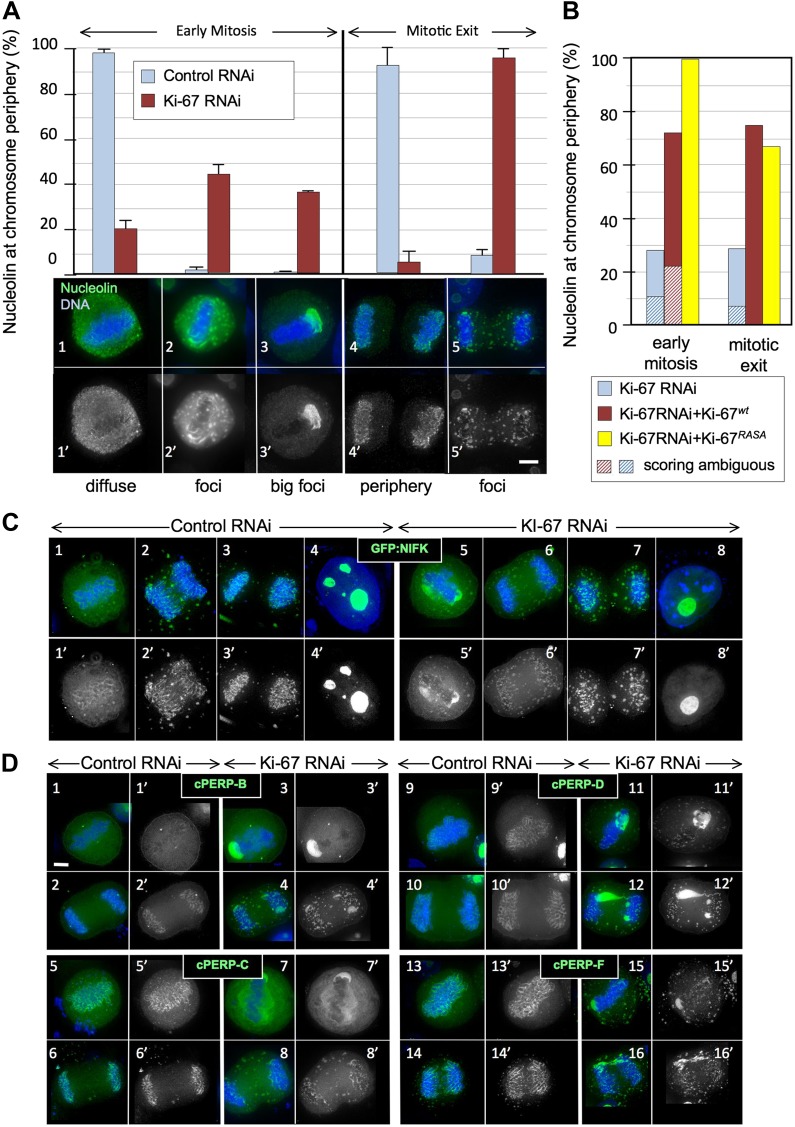
Figure 2. Ki-67 is required for targeting of nucleolar proteins to the chromosome periphery in mitosis.
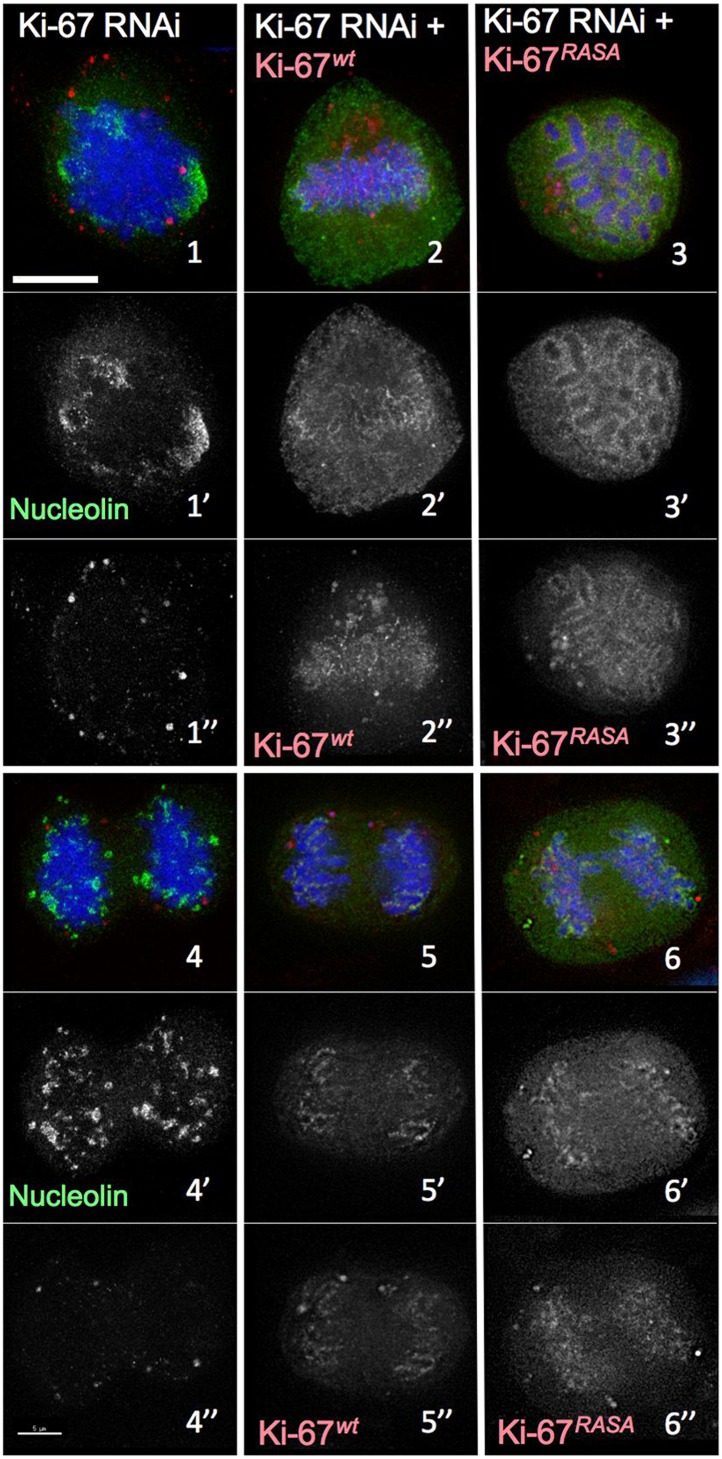
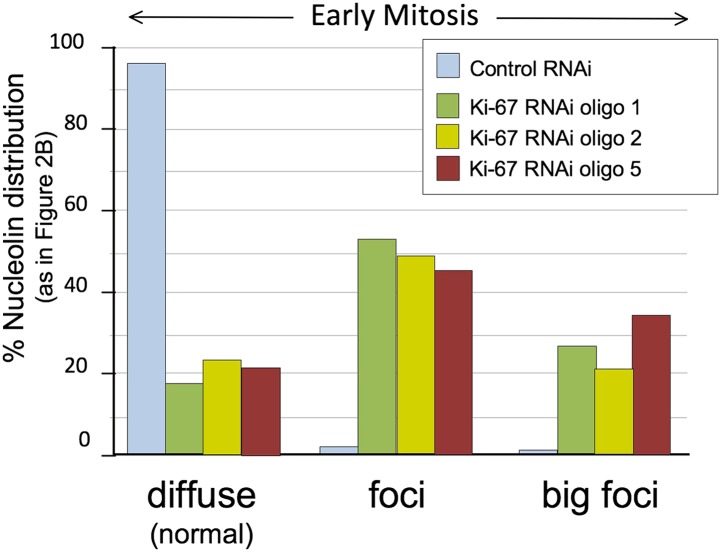
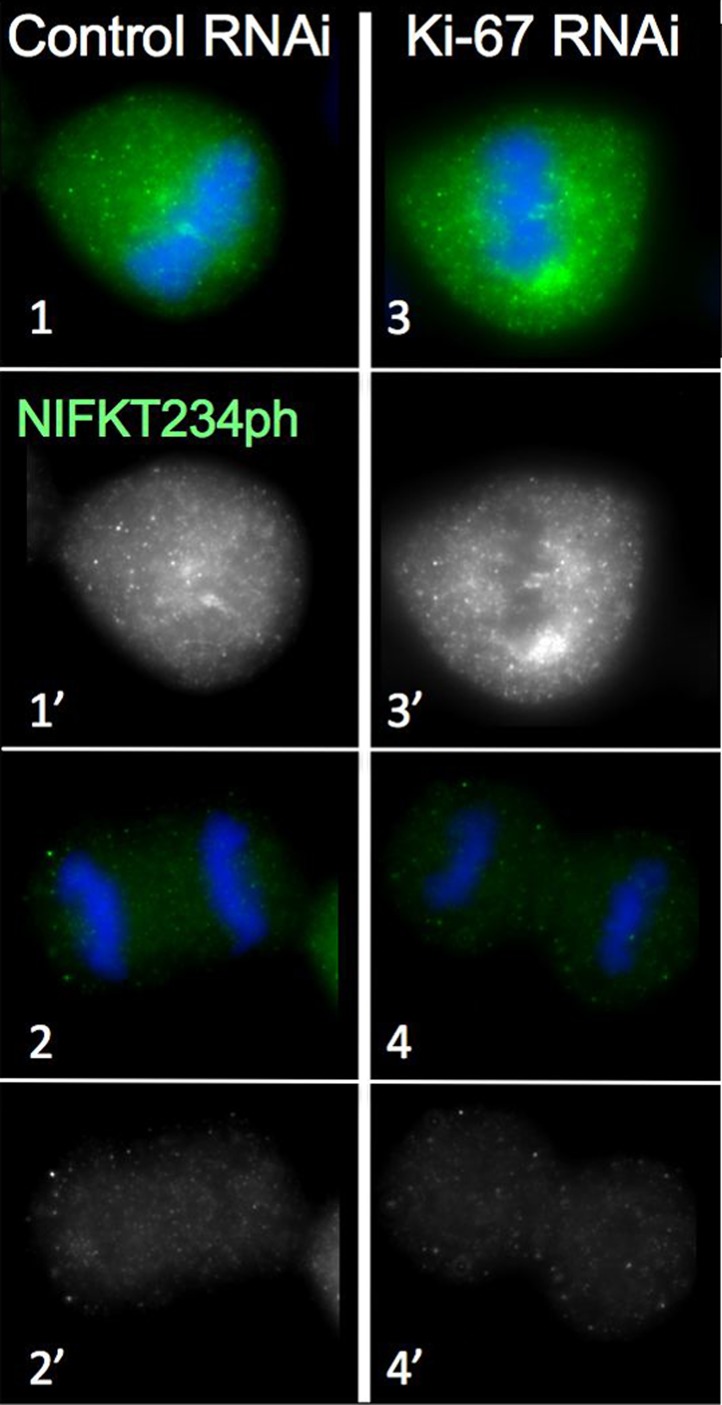
(A) Localisation of endogenous nucleolin is aberrant in mitotic cells after Ki-67 depletion (panels 2, 3, 5). HeLa cells were transfected with Ki-67 RNAi oligo 5 (panels 2, 3, 5) or control oligos (panels 1, 4) and stained for nucleolin (green). Quantification of the phenotypes is indicated in the graph above the corresponding representative images. Scale bar 5 μm. (B) RNAi rescue experiment. HeLa cells depleted of Ki-67 were transfected with either mCherry:Ki-67wt, or mCherry:Ki-67RASA, together with Ki-67 RNAi oligo 5 or control oligo and stained for nucleolin. The localisation of nucleolin in mitotic cells was quantified in the different experimental conditions. See Figure 2—figure supplement 1 for representative images. Scale bar 10 μm. (C) The mitotic chromosome peripheral localisation of NIFK is disrupted upon Ki-67 RNAi (panels 5–6). HeLa cells were transfected with GFP:NIFK (green) and oligo 5 (panels 5–8) or control oligo (panels 1–4). Scale bar 10 μm. (D) All novel cPERPs tested failed to accumulate on the chromosome periphery in mitosis. HeLa cells were co-transfected with GFP:cPERPs identified in an earlier study (Ohta et al., 2010) (green) and oligo 5 (panels 3–4, 7–8, 11–12, 15–16) or control oligo (panels 1–2, 5–6, 9–10, 13–14): GFP:cPERP-B (panels 1–4), GFP:cPERP-C (panels 5–8), GFP:cPERP-D (panels 9–12), GFP:cPERP-F (panels 13–16). Scale bar 5 μm.