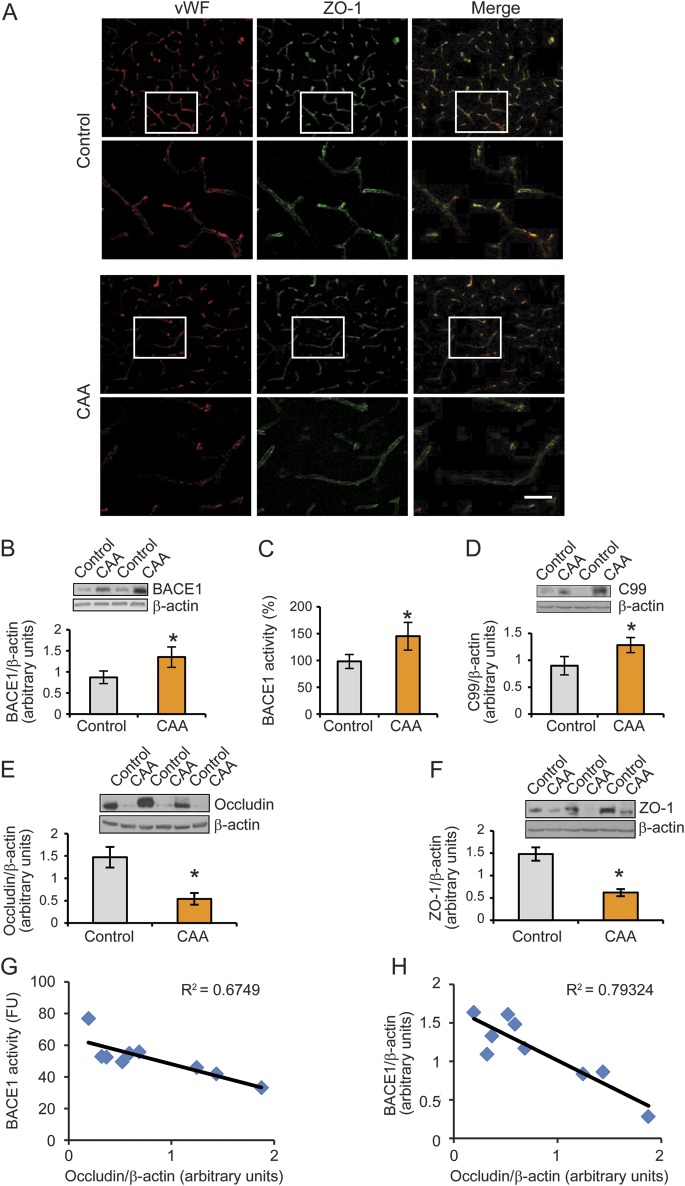
Figure 3. Elevation of BACE1 protein levels and enzymatic activity are associated with the deficiency of tight junction proteins in the cortex and leptomeningeal vessels of patients with CAA.
(A) Reduced ZO-1 expression was observed in the cortical vessels of the CAA group compared with controls. Bar: 20 μm. (B, C) BACE1 protein expression and activities were demonstrated in the leptomeningeal vessels of controls and subjects with CAA. (D) An increased expression of C99, the C-terminal fragment cleaved from amyloid precursor protein by BACE1, was shown in leptomeningeal vessels of patients with CAA compared with those in control individuals. (E, F) The expressions of both occludin and ZO-1 were decreased in CAA leptomeningeal vessels compared with controls. (G) The BACE1 activity in the leptomeningeal vessels of subjects with CAA was negatively correlated with occludin protein levels. (H) BACE1 protein levels were negatively correlated with occludin protein levels in the leptomeningeal vessels of subjects with CAA. All data are the mean ± SD of 3 independent measurements. Error bars represent SD. *p < 0.05 vs control sample. BACE1 = β-site APP-cleaving enzyme 1; CAA = cerebral amyloid angiopathy; vWF = von Willebrand factor.