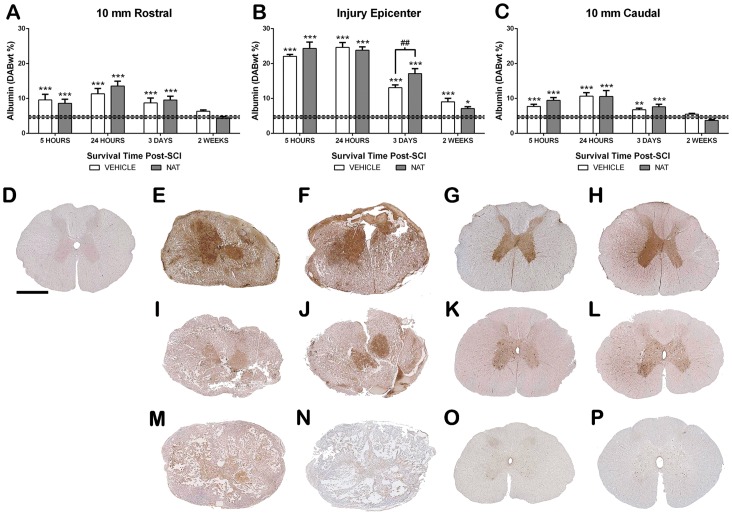
Figure 8. The effect of NAT treatment on albumin immunoreactivity following SCI.
Albumin immunoreactivity at 10(A), within the injury epicentre (B) and at 10 mm caudal (C). Sham sections (D) demonstrated minimal immunoreactivity. Immunoreactivity was significantly increased at both 5 and 24 hours post-SCI. Representative images at 24 hours are shown within the injury epicentre (E-vehicle, F-NAT) and adjacent segment (G-vehicle, H-NAT). By 3 days post-SCI albumin immunoreactivity began to reduce within the injury epicentre (I-vehicle, J-NAT) and adjacent segment (K-vehicle, L-NAT), though NAT treatment resulted in significantly greater albumin immunoreactivity when compared to vehicle. Albumin immunoreactivity reduced further by 2 weeks post-SCI within the injury epicentre (M-vehicle, N-NAT), returning to sham levels within the adjacent segments (O-vehicle, P-NAT). *denotes p<0.05, **denotes p<0.01, ***denotes p<0.001 when compared to sham. Mean sham values indicated by the dashed line. Scale bar = 1 mm.