Figure 4.
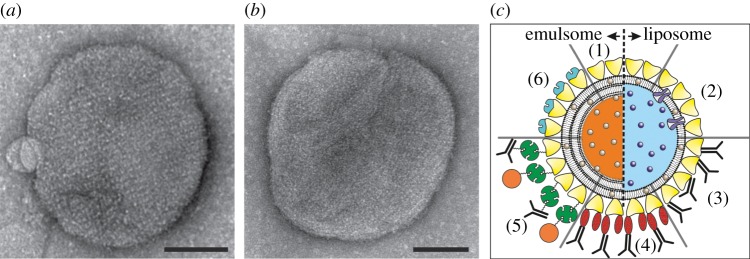
Left: Transmission electron microscopy images of emulsomes coated with the S-layer protein SbsB from G. stearothermophilus PV72/p2 (a) wild-type SbsB and (b) recombinant SbsB. The bars correspond to 100 nm. (Adapted from [19]. Copyright © 2013 with permission from Wiley-VCH.) (c) Schematic drawing of (1) an S-layer-coated emulsome (left) and Iiposome (right) with entrapped functional molecules and (2) functionalized by reconstituted integral proteins. Note, S-layer-coated emulsomes can only transport hydrophobic molecules but with a much higher transport capacity. S-layer-coated emulsomes and liposomes can be used as an immobilization matrix for functional molecules (e.g. human immunoglobulin G) either by direct binding (3) or by immobilization via the Fc-specific ligand protein A (4), or biotinylated ligands can be bound to the S-layer-coated liposome or emulsomes via the biotin–avidin system (5). Alternatively, emulsomes or liposomes can be coated with genetically modified S-layer subunits incorporating functional domains (6). (Adapted from [20]. Copyright © 2002 with permission from Wiley-VCH.)
