Figure 5.
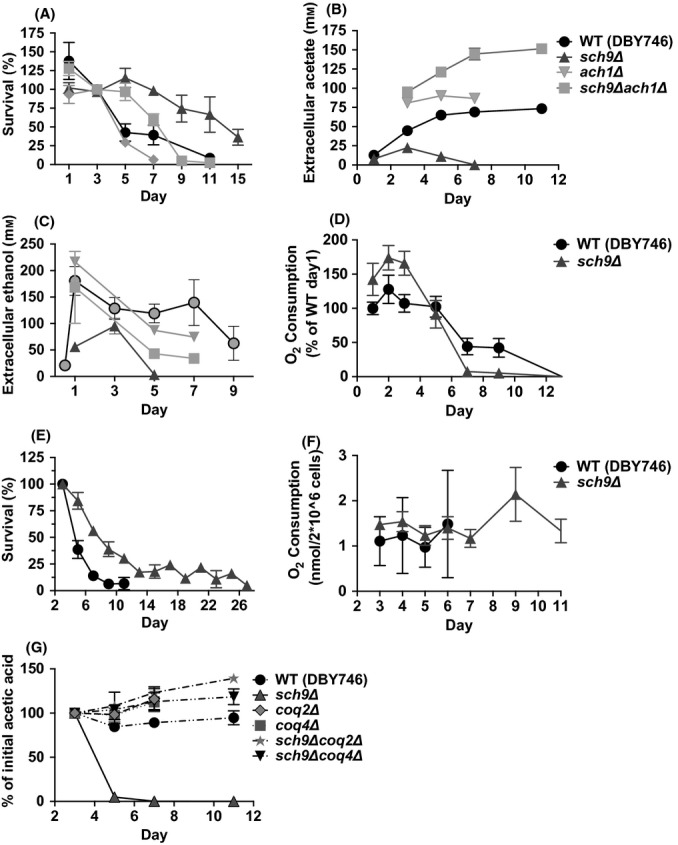
Ach1 and electron transport activities are important for acetic acid utilization. (A) Chronological survival of wild-type, ach1∆, sch9∆, and sch9∆ach1∆ mutants (n = 7). (B, C) Extracellular acetic acid and ethanol concentrations during chronological aging (n = 4). (D) O2 consumption of wild-type (DBY746) and sch9Δ mutants during chronological aging. Data are presented as mean ± SE (n = 8–9). (E, F) WT (DBY746) and sch9Δ mutants were grown in SDC and switched to the carbon source mix medium (40 mm MES buffer, pH 3.7: with 50 mm acetic acid and 141 mm ethanol). The medium was changed on day 3 and replaced every other day. Chronological survival and O2 consumption were monitored for the entire chronological lifespan study. Data are presented as mean ± SEM (n = 7). (G) WT and deletion mutants were switched to 40 mm MES buffer (pH 3.7) containing 25 mm acetic acid. Acetate utilization was monitored.
