Fig. 7. Schematic representation of the fate of WT1+ progenitors during development and adulthood.
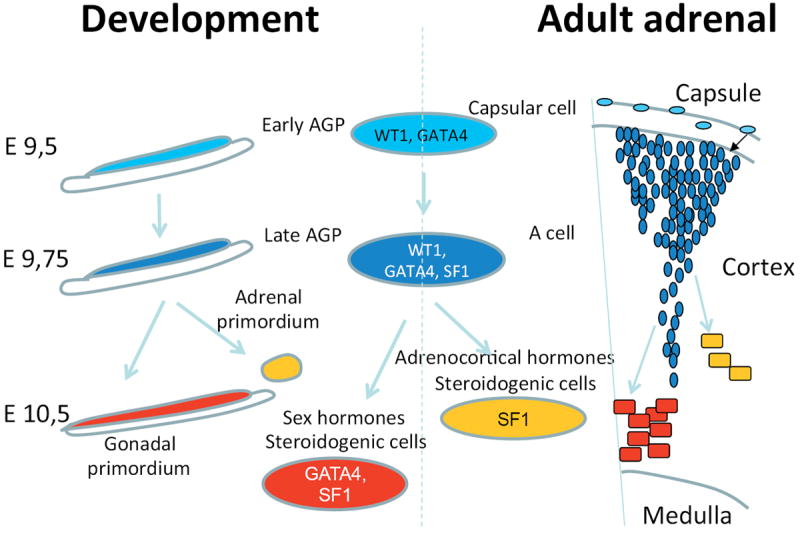
Our data expose clear parallels between mechanisms that drive adrenogonadal development and the differentiation of AGP-like cells in the adult adrenal cortex. Progenitor cells are characterized by WT1 and GATA4 expression. WT1 prevents differentiation by regulating expression of key genes such as GLI1 and TCF21. Suppression of WT1 is thus a key step to allow steroidogenic differentiation both during development and or adult AGP-like cells. Upon gonadectomy AGP-like cells respond by differentiating into gonadal steroidogenic cells.
