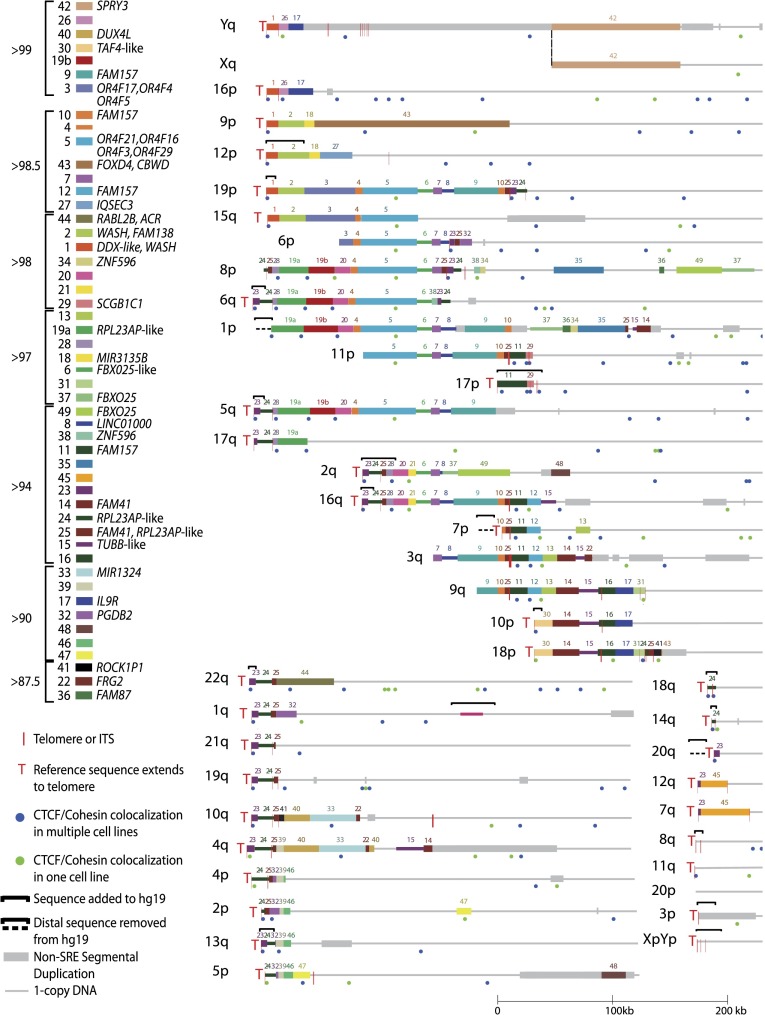
Figure 1.
Sequence organization of updated subtelomere sequence assemblies. The assemblies are oriented with the telomere on the left and aligned to maximize paralogous blocks of SREs following the methods described in Linardopoulou et al. (2005). Regions of the assemblies differing from hg19 are indicated by the black brackets above the altered region of the assembly. An internal gap in the 1q assembly is indicated by the magenta line segment. The pseudoautosomal region of Xq and Yq shares the same reference sequence and is indicated by the thick gray line distal to the dotted line. Blocks 43 and 44 are shown as subtelomere paralogs because they are duplicated at the 2q site of an ancestral telomere fusion; other internal paralogies are not shown or analyzed here. A selection of named transcripts mapping primarily to the indicated blocks is listed; a much larger number of uncharacterized transcripts and ncRNAs is not shown here but is annotated on the subtelomere browser. The average percentage of identity shared by copies of paralogous blocks is indicated by the groupings to the left of the color key. The positions of telomeres, ITSs, and CTCF/cohesion colocalization sites in the three cell types examined in detail are as indicated in the figure.