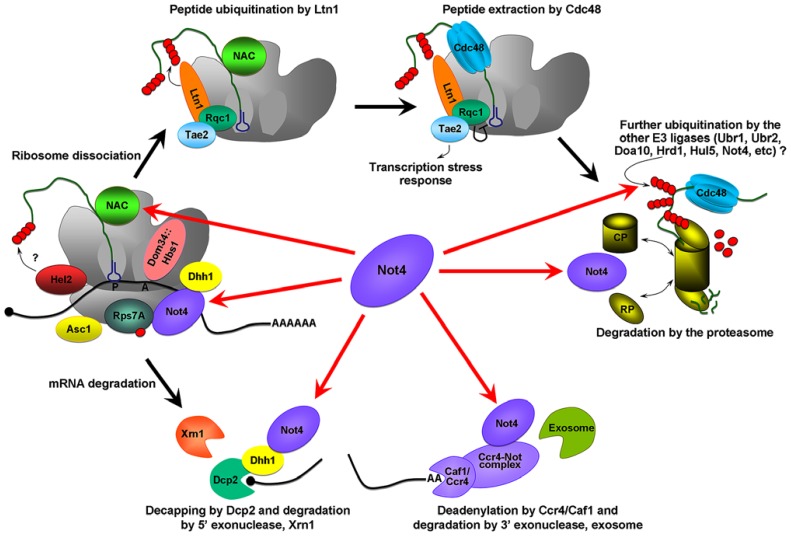
FIGURE 1.
Possible roles of Not4 in cotranslational QC. The Hbs1/Dom34 complex binds the empty A site on the stalling ribosome and stimulates the endonuceolytic mRNA cleavage, and separation of the stalled ribosomes. The 40S ribosome binding protein Asc1/RACK1, and E3 ligase, Hel2, were identified as proteins involved in QC and acting before ribosome dissociation (Kuroha et al., 2010; Brandman et al., 2012; Duttler et al., 2013). Hel2 could initiate ubiquitination of the nascent chain. Further ubiquitination is associated with Ltn1 (Defenouillere et al., 2013). Ltn1 together with proteins Tae2 (translation-associated element 2), Rqc1 (ribosome quality control 1), and the disaggregase Cdc48 forms a RQC complex (ribosome QC complex; Brandman et al., 2012; Defenouillere et al., 2013). Cdc48 extracts the peptide from the 60S, Rqc1 regulates the activity of the RQC by a negative feedback loop, and Tae2 signals translational stress to the corresponding transcription factors (Brandman et al., 2012). Extracted peptides are probably subjected to further ubiquitination by other E3 ligases and finally degraded by the proteasome. The red arrows indicate the possible pathways by which Not4 may act. Not4 may ubiquitinate translationally arrested peptides. It may also be involved in the clearance of arrested protein products by the proteasome. Not4 may preserve translation acting through several targets; the deadenylase module of the Ccr4-Not complex, Dhh1, the ribosome-associated chaperone, NAC, and through the ubiquitination of Rps7A. Finally, Not4 may interact with mRNA and “sense” ribosome pausing and/or recruit the factors necessary for correct translation.