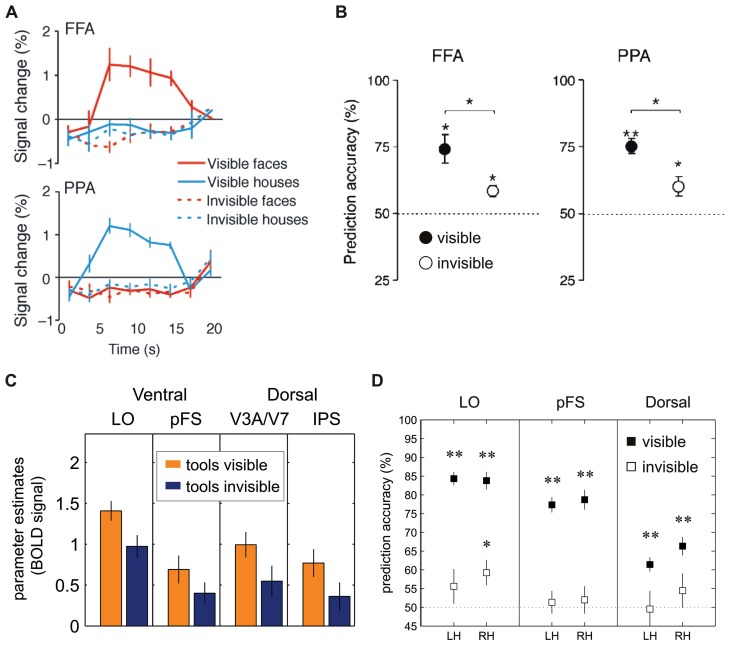
FIGURE 4.
Univariate and multivariate analysis of FMRI-BOLD activation to visual stimuli suppressed by CFS. (A) Sterzer et al. (2008): The fusiform face area (FFA) and the parahippocampal place area (PPA) in inferior temporal cortex showed significantly reduced BOLD activity levels whenever images of faces or houses were rendered invisible. (B) Sterzer et al. (2008): Performance of support-vector-machine (SVM) classifiers for pairwise classification of face and house presentations from FFA and PPA. Filled circles: visible trials; open circles: invisible trials. (C) Hesselmann and Malach (2011): BOLD signals (parameter estimates in arbitrary units) to images of tools in dorsal and ventral visual areas show stream-invariant reduction whenever stimuli were rendered invisible (LO = lateral occipital area, pFS = posterior fusiform gyrus, IPS = intra-parietal sulcus). (D) Hesselmann and Malach (2011): Performance of SVM classifiers in left hemisphere (LH) and right hemisphere (RH) dorsal and ventral visual areas. Prediction accuracies in visible trials (filled squares) were significant in all regions-of-interest; in invisible trials (open squares), area LO showed classification performance significantly above chance level (*p < 0.01; **p < 0.001). (A,B) Reproduced from Sterzer et al. (2008; copyright 2008 Association for Research in Vision and Ophthalmology). (C,D) Modified from Hesselmann and Malach (2011; copyright 2011 Oxford University Press).