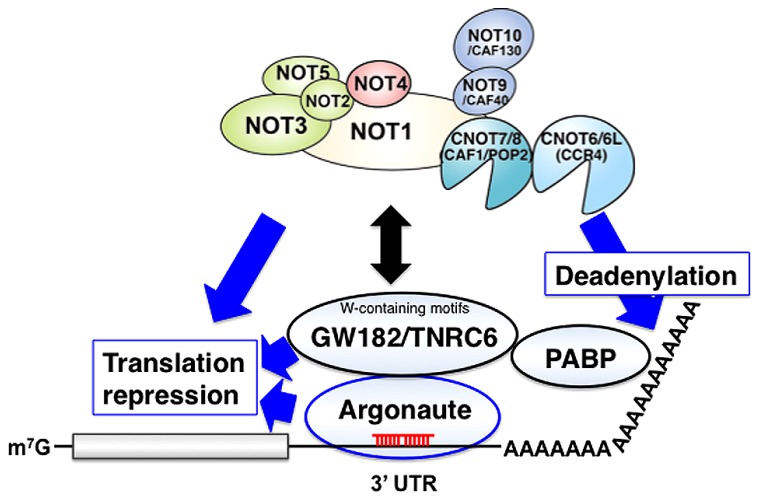
FIGURE 2.
The CCR4-NOT complex functions in gene silencing by miRNA. MicroRNA (miRNA)-induced silencing complexes (miRISCs) on target mRNA contain both miRNA (red) and an Argonaute protein. The Argonaute protein interacts with a GW182/TNRC6 family protein, and these factors play crucial roles in miRNA-induced gene silencing including deadenylation, translational repression and the rapid decay of mRNA targets. Potential roles of CCR4-NOT in miRISCs: Deadenylation: GW182/TNRC6-mediated recruitment of CCR4-NOT requires conserved W-containing motifs of GW182/TNRC6, and C-terminal effector domain of GW182/TNRC6 is sufficient to bind CCR4-NOT and promote deadenylation of target mRNAs. Association of the CCR4-NOT complex with the GW182/TNRC6 protein releases PABP from the mRNA poly(A) tail, thereby disrupting mRNA circularization and facilitating translational repression and deadenylation. Translation repression: MicroRNA-induced translation repression occurs independent of deadenylation by CCR4-NOT in various organisms. The molecular mechanism by which miRISC inhibits translation is still largely unknown. Decapping: miRISC also triggers decapping and the subsequent degradation of mRNA targets independently of ongoing deadenylation. CCR4-NOT may be involved in this regulation.