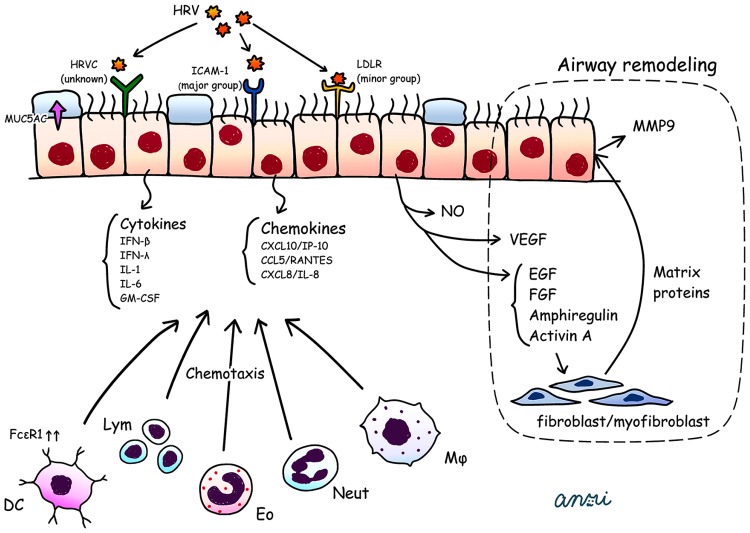
FIGURE 1.
HRV attaches to airway epithelial cells via ICAM-1, LDLR, and unknown receptors for HRV-C. HRV infected bronchial epithelial cells secrete a wide range of cytokines (IFN-β, IFN-λ, IL-1, IL-6, GM-CSF) and chemokines (CXCL10/IP-10, CCL5/RANTES, CXCL8/IL-8) together with NO, VEGF, and EGF, FGF, amphiregulin and activin A. These cytokines and chemokines attract various inflammatory cells such as DCs with upregulation of FcεR1, lym, Eo, Neut, and Mϕ. The VEGF, EGF, FGF, amphiregulin and activin A promote the release of matrix proteins from fibroblasts/myofibroblasts, which enhance the production of MMP9 from airway epithelial cells. These phenomena could lead to airway remodeling (dotted area; i.e., thickening of the lamina reticularis). HRV infection induces secretion of MUC5AC, which impairs mucociliary clearance. DCs, dendritic cells; EGF, epidermal growth factor; Eo, eosinophil; FGF, fibroblast growth factor; GM-CSF, granulocyte macrophage colony-stimulating factor; ICAM-1, intercellular adhesion molecule 1; LDRL, low-density lipoprotein receptor; Lym, lymphocyte; MMP, matrix metalloproteinase; Mϕ, macrophage; Neut, neutrophil; NO, nitric oxide synthase; RANTES, regulated on activation, normal T cell expressed and secreted; VEGF, vascular endothelial growth factor.