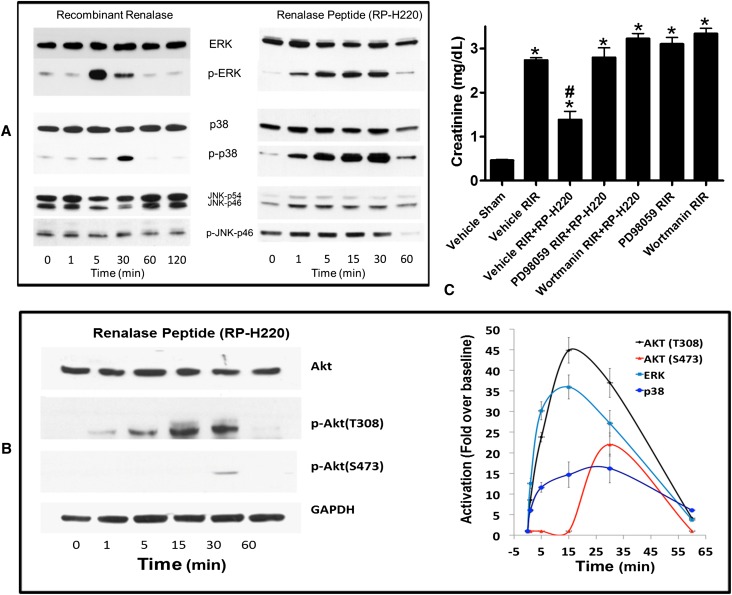
Figure 4.
MAPK activation is critical for the protective effect renalase peptides. (A) MAPK signaling by renalase and renalase peptides. Western blot analysis; representative blot (n=3). JNK, c-Jun N-terminal kinases; p, phosphorylated, activated proteins. (B) Renalase activates AKT. Left panel: Western blot analysis; representative blot (n=3). Right panel: signals normalized to glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase loading control (n=3). Change over baseline statistically significant at P<0.05 from 1 to 60 minutes for ERK, p38, and AKT (T308) and at 30 minutes only for AKT (S473). (C) ERK or AKT inhibition abrogates protective effect of RP-H220. Plasma creatinine levels from mice subjected to sham surgery or to renal ischemia and reperfusion (RIR); renalase WT mice were subjected to sham surgery or to 30 minutes of renal ischemia and reperfusion. For mice subjected to renal ischemia and reperfusion, RP-H220 or vehicle (saline) was injected 10 minutes before renal ischemia. Some animals were pretreated with the ERK inhibitor PD98059 or the PI3K/AKT inhibitor wortmannin (n=6–8 per group, *P<0.05 versus vehicle-treated mice subjected to sham surgery; #P<0.05 versus vehicle-treated WT mice subjected to renal ischemia and reperfusion).