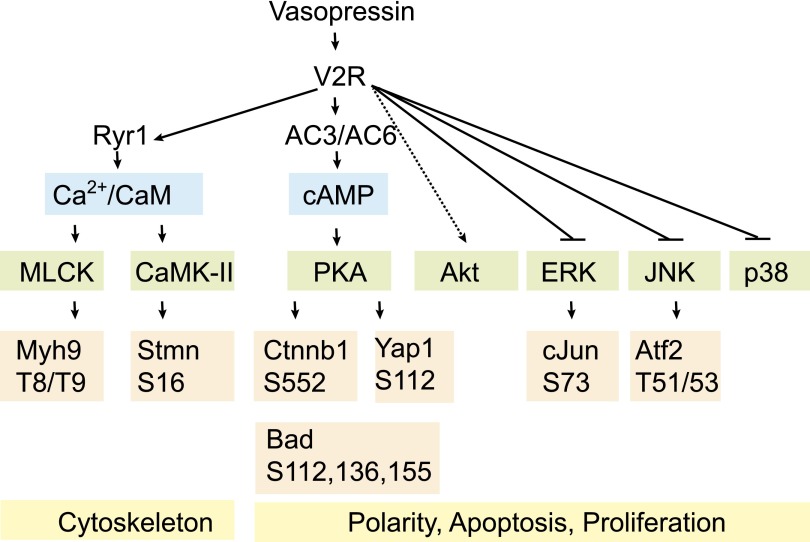
Figure 1.
A simplified view of V2R-dependent signaling in collecting duct cells revealed by phosphoproteomic and protomic approaches in various vasopressin-responsive tissues in vivo, ex vivo, and in vitro. The studies show alterations in cytoskeletal protein phosphorylation (e.g., Myh9 and Stmn). In addition, proteins involved in the maintenance of polarity and proliferative tone are significantly affected on functional phosphorylation sites. AC, adenylate cyclase; Atf2, activating transcription factor 2; Bad, Bcl2-agonist of cell death; CaM, calmodulin; CaMK-II, calmodulin-dependent kinase 2; cJun, proto-oncogene c-Jun; Ctnnb1, β-catenin; JNK, c-Jun N-terminal kinase; MLCK, myosin light chain kinase; Myh, myosin heavy chain; Ryr, ryanoidin receptor; Stmn, Stathmin; Yap1, yorkie homolog protein 1.