Figure 2.
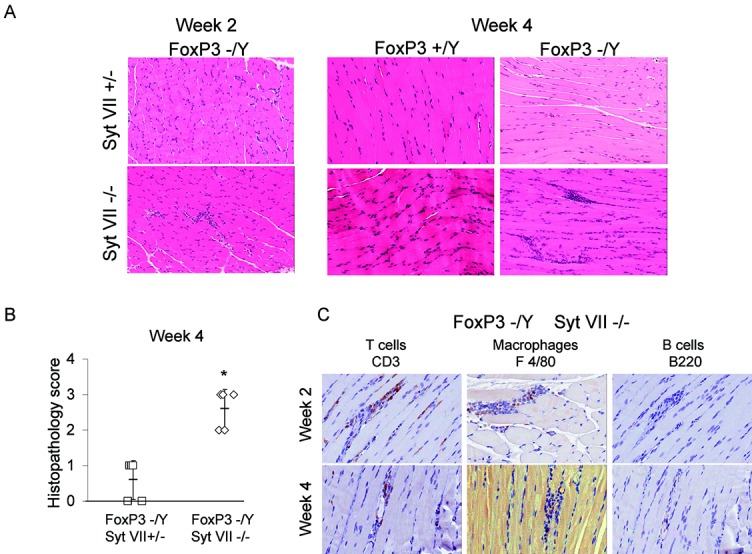
FoxP3 and synaptotagmin VII (Syt VII) double-mutant mice develop significant myositis. Male Syt VII+/− mice were bred with female FoxP3+/− mice to produce male wild-type, Syt VII mutant (Syt VII−/−), FoxP3 mutant (FoxP3−/Y), and double-mutant (Foxp3−/Y/Syt VII−/−) mice. A, Hematoxylin and eosin–stained muscle sections obtained from mice killed at 2 weeks or 4 weeks (±2 days). Original magnification × 200. B, Extent of myositis in Foxp3−/Y/Syt VII+/− and Foxp3−/Y/Syt VII−/− mice at the 4-week time point. Each symbol represents an individual mouse. Bars show the mean ± SD. C, Immunohistochemical staining for CD3 (T cell marker), F4/80 (macrophage cell marker), and B220 (B cell marker) in muscle sections obtained from FoxP3/Syt VII double-mutant mice at the 2-week and 4-week time points. Original magnification × 400. Results are representative of observations made in at least 3 mice at each time point and were independently verified in subsequent experiments. ∗ = P ≤ 0.005 versus Syt VII+/−.
