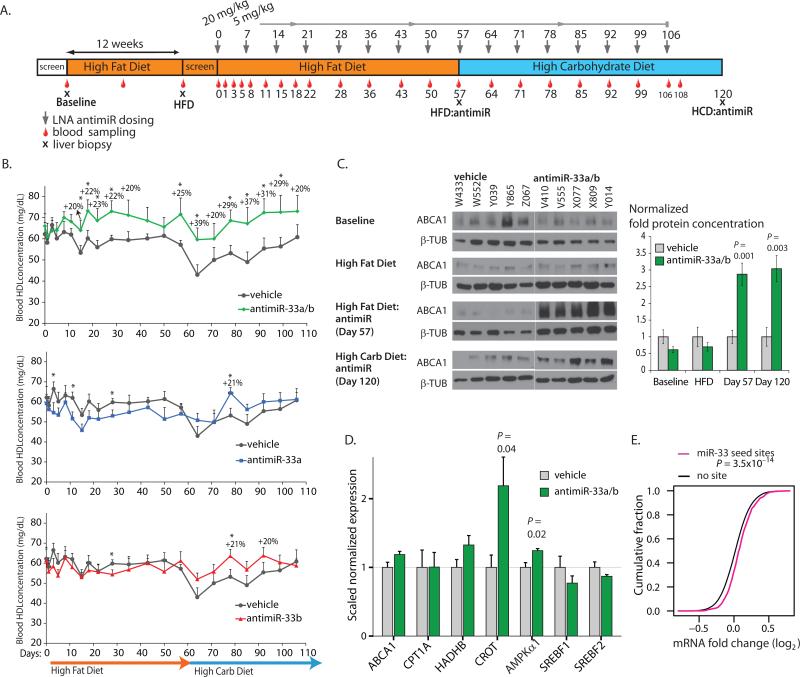
Fig. 2. Inhibition of the miR-33 family in obese African green monkeys by a seed-targeting 8-mer antimiR oligonucleotide.
(A) Design and timeline of the non-human primate study. (B) Plasma HDL-C concentrations in antimiR-33a/b-, antimiR-33a- and antimiR-33b-treated African green monkeys compared to vehicle control-treated animals. * represents P <0.05. P-values are given in table S2. (C) Western blot analysis of hepatic ABCA1 protein in vehicle- and antimiR-33a/b-treated African green monkeys. (D) De-repression of miR-33 target mRNAs in antimiR-33a/b-treated African green monkeys. Error bars represent standard error of the mean (SEM). Statistical analysis was performed with Student's t-test. (E) De-repression of liver mRNAs with predicted miR-33 seed match sites in antimiR-33a/b-treated monkeys compared to vehicle-treated control animals. Cumulative distributions of mRNA changes between antimiR-33a/b- and vehicle-treated animals are shown for TargetScan 6.2-predicted miR-33 target mRNAs (magenta) and mRNAs without miR-33 seed match sites (black), demonstrating that miR-33 target mRNAs are de-repressed in monkey livers after antimiR-33a/b treatment (P = 3.5x10-14, one sided Kolmogorov-Smirnov test).