Fig. 4.
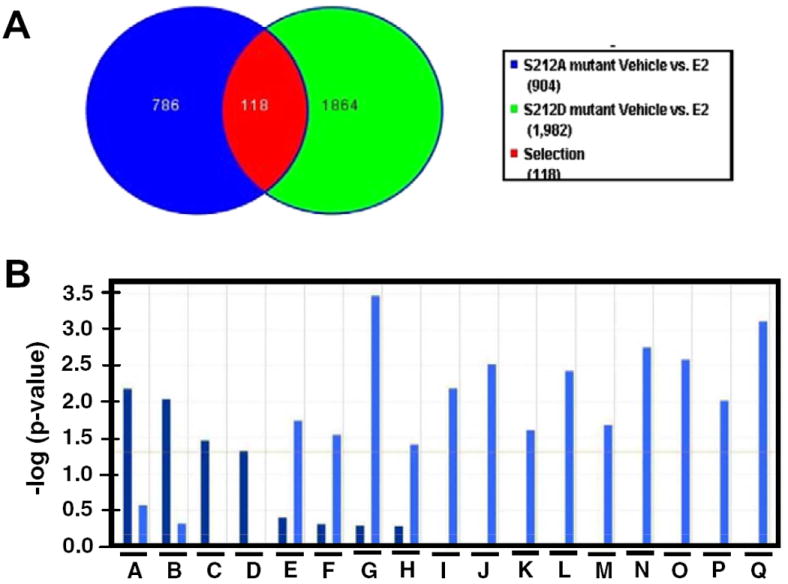
Differential gene regulation by ERα S212A and ERα S212D. (A) Venn diagram illustrating the number of specific and common genes regulated by the two ERα mutants. (B) Gene ontology analysis (IPA) for significant canonical pathways. A, arylhydrocarbon receptor signaling; B, tumoricidal function of hepatic natural killer cells; C, LPS/IL-1 mediated inhibition of RXR function; D, IL-6 signaling; E, dendritic cell maturation; F, communication between innate and adaptive immune cells; G, OX40 signaling pathway; H, regulation of IL-2 expression in activated and anergic T lymphocytes; I, CTLA4 signaling in cytotoxic T lymphocytes; J, T helper cell differentiation; K, IL-9 signaling; L, CD28 signaling in T helper cells; M, ICOs-ICOSL signaling in T helper cells; N, Crosstalk between dendritic cells and natural killer cells; O, PKCδ signaling in T lymphocytes; P, MSP-ROH signaling pathway; Q, antigen presentation pathway. Bars in darker blue and in lighter blue represent signaling pathways that were regulated by ERα S121A and ERα S212D, respectively.
