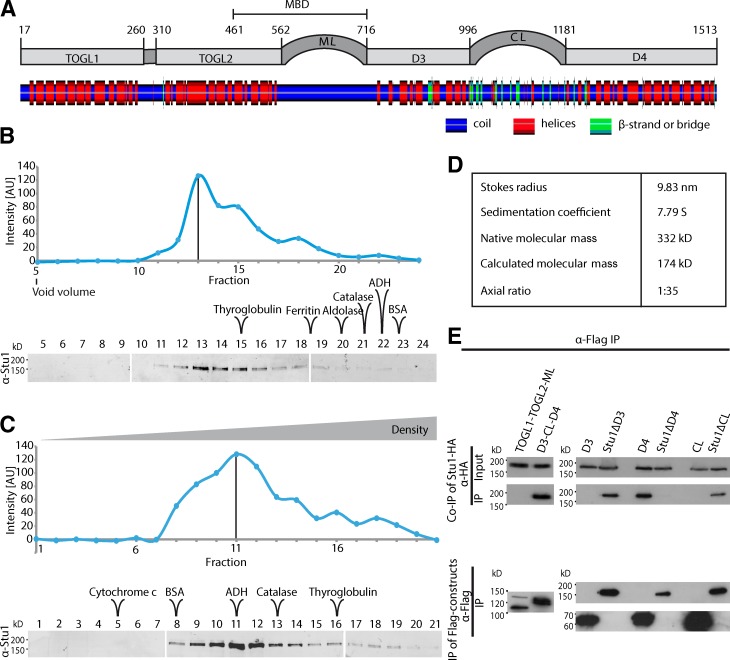
Figure 1.
Stu1 dimerizes via D4. (A) Putative domain organization of Stu1. Secondary structure prediction was performed using SYMPRED and visualized by POLYVIEW-2D (Porollo et al., 2004). (B–D) Stu1 is a dimer with an elongated rod shape. The data shown are from a single representative experiment out of two analyses. (B) Gel filtration analysis of FLAG-Stu1. (C) Sucrose gradient analysis of FLAG-Stu1. (B and C) The samples were run on three separate gels as shown. Fractions containing Stu1 were detected by Western analysis and quantified. Standard proteins as indicated were used to determine the Stokes radius or sedimentation coefficient of Stu1 (see also Fig. S1, A and B). White lines indicate that intervening lanes have been spliced out. The black lines indicate the peak fraction. AU, arbitrary unit. (D) Native molecular mass and axial ratio of Stu1 as calculated from the determined hydrodynamic properties as previously described (Schuyler and Pellman, 2002). (E) D4 is the dimerization domain. FLAG-Stu1-GFP constructs were coexpressed with Stu1-HA in S. cerevisiae, and FLAG-Stu1-GFP constructs were affinity purified.