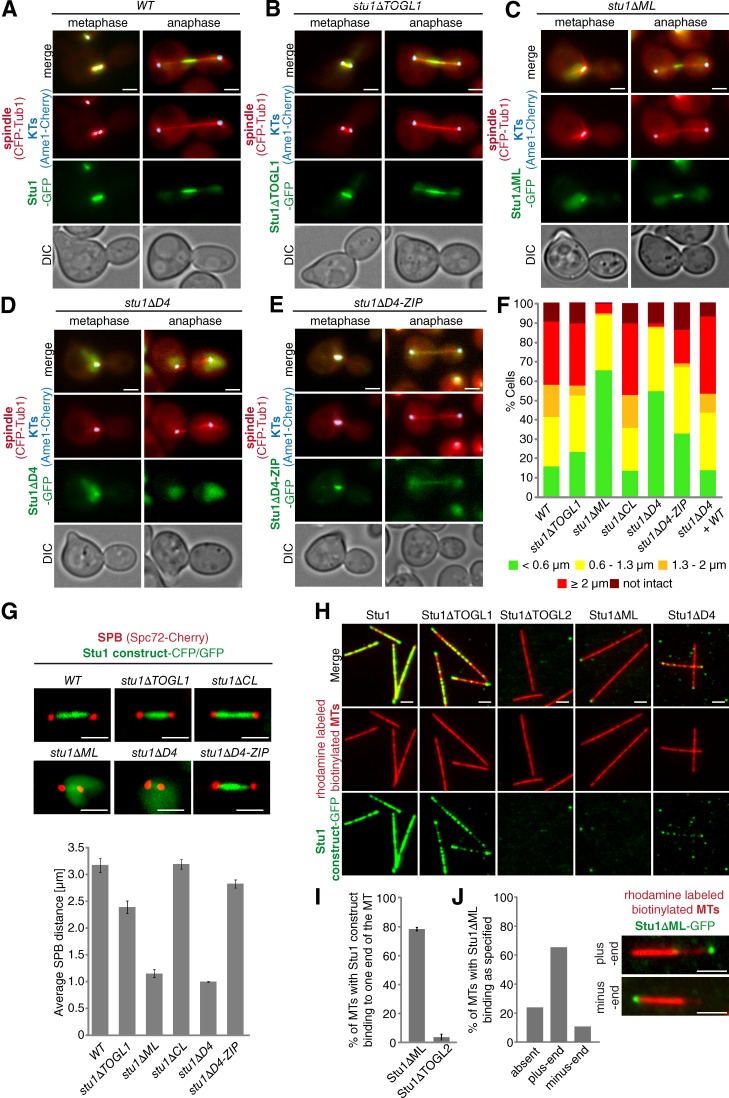
Figure 6.
ML and TOGL2 confer interaction of Stu1 with the MT lattice. (A–G) Localization to metaphase spindles depends on ML and Stu1 dimerization. (A–E) Cells were released from G1 arrest and visualized in metaphase and anaphase. DIC, differential interference contrast. (F) Spindle phenotypes were quantified as indicated 2 or 2.5 h (Fig. S2) after G1 release. n > 100. (G) Cells were arrested in metaphase by Cdc20 depletion for 5 h. Spindle length was measured as the distance between SPB signals for n > 100. Error bars represent SDs for two experiments. (H) ML and TOGL2 confer MT lattice binding in vitro. Stabilized and immobilized MTs were incubated with purified Stu1 constructs (Fig. S5 A) and visualized as indicated. (I and J) TOGL2 confers MT plus-end binding in vitro. (I) Quantification of MTs with Stu1 at one of the ends. Experiment performed as in H. Error bars represent the SDs of two experiments. n > 150. (J) Quantification of MTs with Stu1 at the plus end. The experiment was performed as in H with the exception that polarity-marked MTs were used. The fraction of MTs with Stu1ΔML bound to plus or minus ends was determined. n = 174 . Bars, 2 µm.