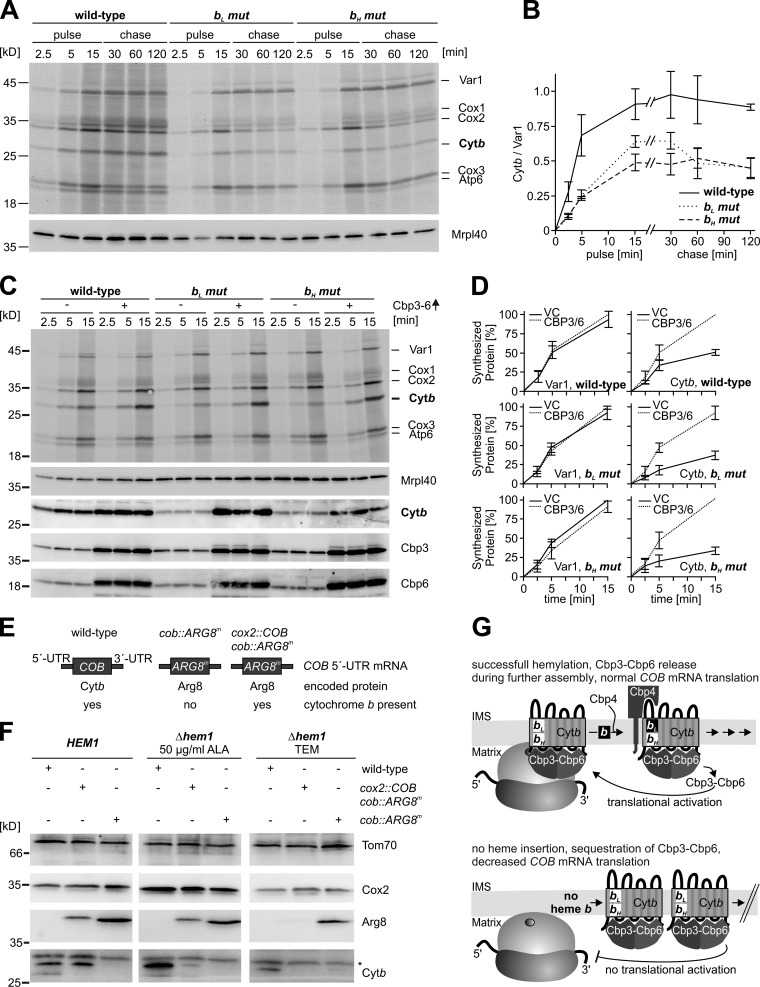
Figure 5.
Failure to hemylate cytochrome b provokes reduction of cytochrome b synthesis through a translational feedback loop. (A) Mitochondrial translation products of the indicated strains were labeled with [35S]-methionine in whole cells. Labeling was stopped by the addition of excess unlabeled methionine. (B) The signals from three independent experiments were densitometrically quantified, normalized to the mean signal for Var1 for each strain, and are presented as mean ± SEM. (C) Cells were transformed either with empty plasmids or with plasmids overexpressing CBP3 and CBP6. Synthesis of mitochondrial translation products was analyzed in whole cells. (D) The signals of cytochrome b or Var1 from three independent experiments ± SEM were densitometrically quantified. The highest value at 15 min was set to 100%. (E) Schematic representation of mRNAs and encoded proteins in the different versions of mitochondrial genomes. (F) The indicated strains were grown for 30 h on YPGal and supplemented with either δ-aminolevulinic acid or TEM. Proteins were extracted and analyzed by Western blotting. The asterisk indicates an unspecific cross-reaction. (G) Model of the feedback loop that down-regulates synthesis of cytochrome b when hemylation fails.