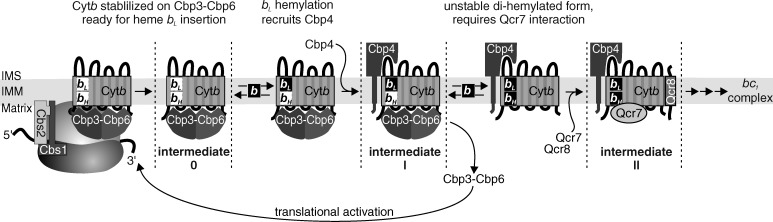
Figure 7.
Model for the stepwise hemylation of cytochrome b. Cytochrome b is synthesized by mitochondrial ribosomes that have the Cbp3–Cbp6 complex bound for efficient translation of the cytochrome b encoding mRNA. Newly synthesized cytochrome b interacts with Cbp3–Cbp6 in an unhemylated form in intermediate 0. Upon hemylation of the bL site, the assembly factor Cbp4 is recruited to stabilize this heme incorporation. Hemylation of the bH site provokes release of Cbp3–Cbp6 and the fully hemylated cytochrome b must interact with Qcr7 for stabilization. Cytochrome b in intermediate II is fully hemylated and ready for further assembly. Hemylation efficiency modulates synthesis of cytochrome b by a feedback loop involving Cbp3–Cbp6 sequestration in assembly intermediates 0 or I. When hemylation proceeds normally, Cbp3–Cbp6 is released for further stimulation of cytochrome b synthesis by mitochondrial ribosomes.