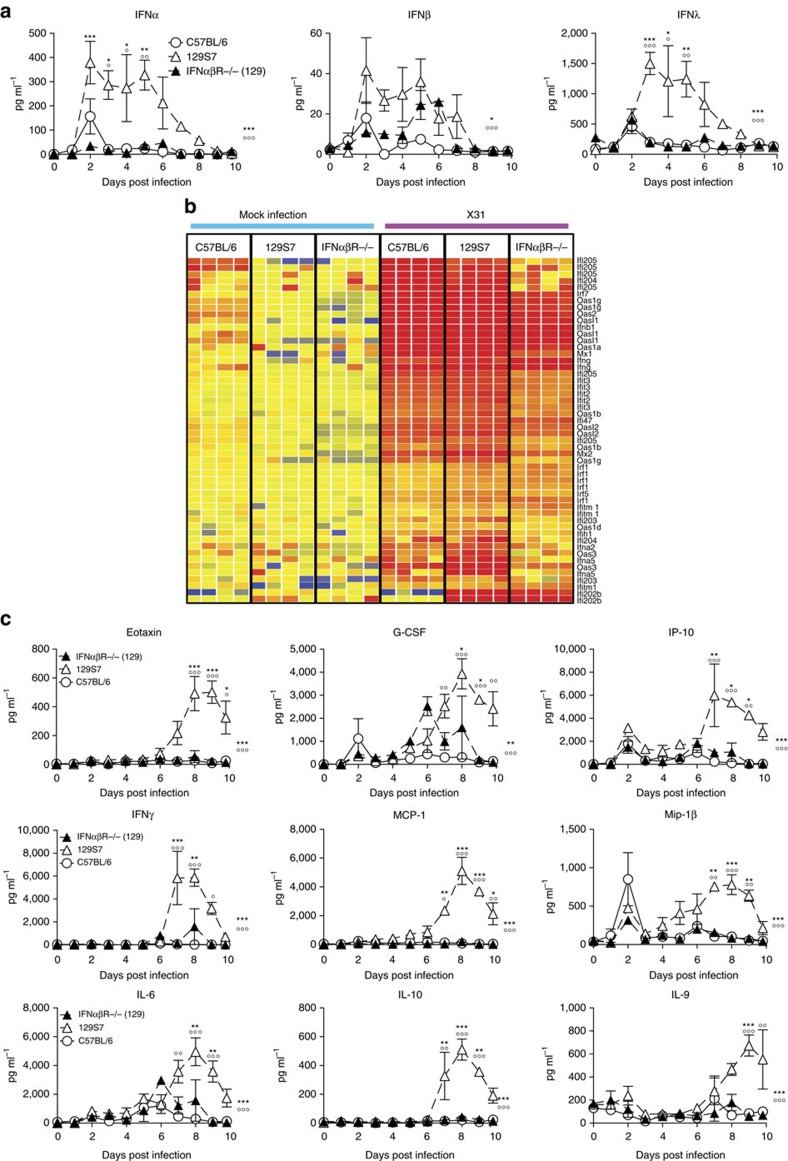
Figure 5. Type I IFN signalling in 129S7 mice leads to high concentrations of proinflammatory cytokines in BAL.
(a–c) 129S7 (open triangles), IFNαβR−/−(129) (filled triangles) or B6 (open circles) mice were infected i.n. with 800 TCID50 of X31. (a) IFN levels in BAL fluid were measured by ELISA and (c) specified pro-inflammatory cytokine concentrations were quantified by Multiplex. (b) Heatmap displaying selected significantly regulated antiviral response genes. Total RNA from mock and X31-infected lung was analysed using Affymetrix Mouse Genome 430 2.0 microarrays at 5 days post infection. Supervised analysis was performed using statistical filtering (≥fourfold change relative to mock-infected C57BL/6; 2-way ANOVA, P<0.01, Benjamini-Hochberg multiple test correction). Graphs show mean±s.e.m. and are representative of two independent experiments where n=3–4. 129:IFNαβR−/−(129) * and 129:B6 ○, where *** or ○○○P<0.0001, ** or ○○P<0.001, *P<0.01 by two-way ANOVA with Bonferroni post tests. The symbols on the right of graphs indicate statistical significance of the whole curve, as tested by two-way ANOVA.