Figure 4.
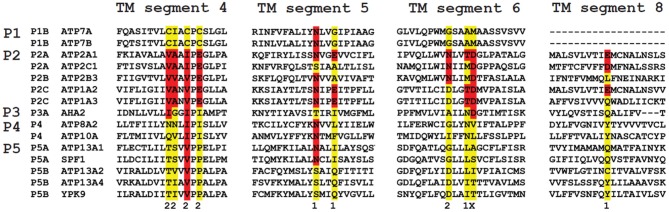
Sequence comparison of the TM helices in P-type ATPases of various subfamilies. The residues involved in Ca2+ binding in the two Ca2+ binding sites (site 1 and 2) in the SERCA1a Ca2+ pump (ATP2A1) are distributed over four TM helices: M4, 5, 6 and 8. The colored residues are part of the Ca2+ binding sites in ATP2A1 and numbers 1 and 2 refer to the number of the Ca2+-binding site to which the residue contributes (x is contributing to both site 1 and site 2). The sequence of the M4, M5, M6 and M8 helices is compared with those of the P-type ATPases that are involved in neurological disorders. Also the yeast P5 ATPases Spf1p and Ypk9p, the Ca2+/Mn2+-ATPase SPCA as well as the proton pump AHA2 are included for comparison. M4 shows the highest degree of conservation. Highlighted in red are conserved residues as compared to the ATP2A1 Ca2+ binding site sequence, whereas in yellow the non-conserved residues are indicated. For each subfamily, a signature motif can be recognized in M4, which corresponds well with the substrate specificity. The PPELP and PPALP sequences of P5A- and P5B-type ATPases have little in common with other P-type ATPase signature motifs, which might indicate that the transported ligand is significantly different.
