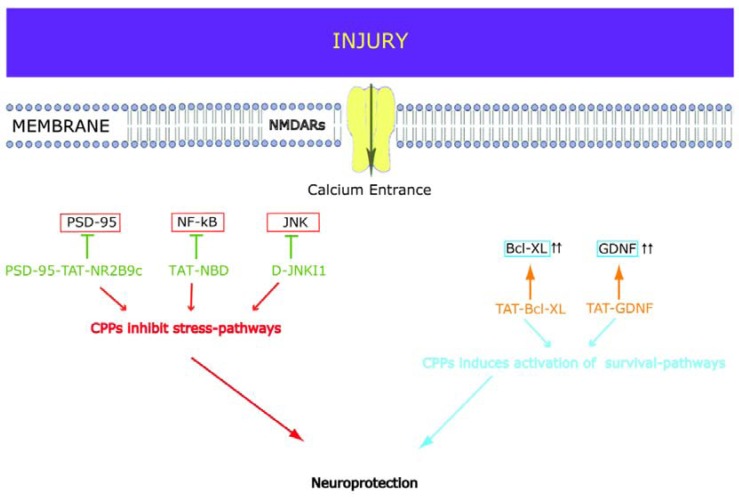
Figure 2.
Schematic representation of the described neuroprotective CPPs and their protein targets. The stress pathways that are triggered by injury and the survival pathways that are activated in neuroprotective mechanisms are presented. We here indicate the two different families of CPPs: inhibitor (⊥) CPPs in red and stabiliser (⇑⇑) CPPs of protective proteins in orange. Inhibitor-CPPs: PSD-95-TAT-NR2B9c blocks the interaction between PSD-95 and the NMDA receptor subunit NR2B. D-JNKI1 blocks the association of JNK with its JBD-targets and inhibits JNK signaling pathways. TAT-NBD inhibits NF-kB activity by blocking association of its key regulators: NEMO (NF-kB essential modulator) with the IKKs (I Kappa B kinases). Stabiliser-CPPs: TAT-Bcl-xL induces Bcl-xL overexpression and subsequently prevents caspase activation. TAT-GDNF induces GDNF stabilization and inhibits caspase activation.