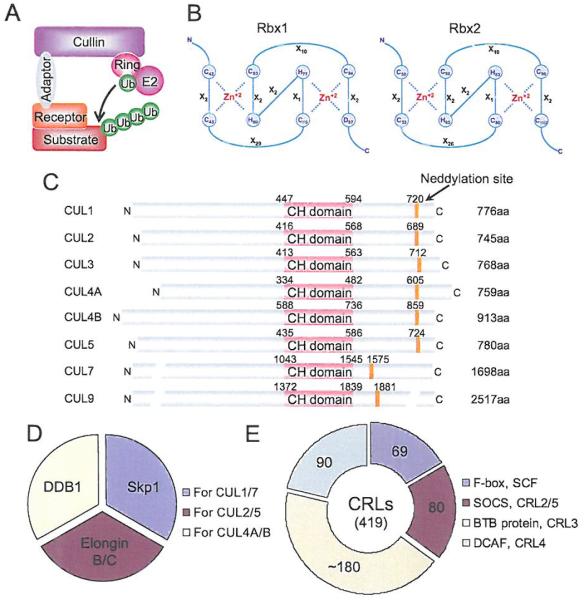
Fig. (3). The composition of CRL E3 ubiquitin ligases.
(A) A typical composition of CRL E3, consisting of a cullin, a RING protein, an adaptor protein, and a substrate recognition receptor. (B) The C3H2C3 RING structure of two RING proteins, RBX1 and RBX2. Numbers represent the amino acid codons and X stands for any amino acid. (C) The domain structure of cullin family members. Numbers represent the amino acid codons. The orange line indicates the position of the neddylation site. (D) Known adaptor proteins in CRLs. (E) The number of the family members in each type of receptor proteins found in CRLs. (The color version of the figure is available in the electronic copy of the article).