Fig. (5). Dynamic regulation of CRLs activity by neddylation.
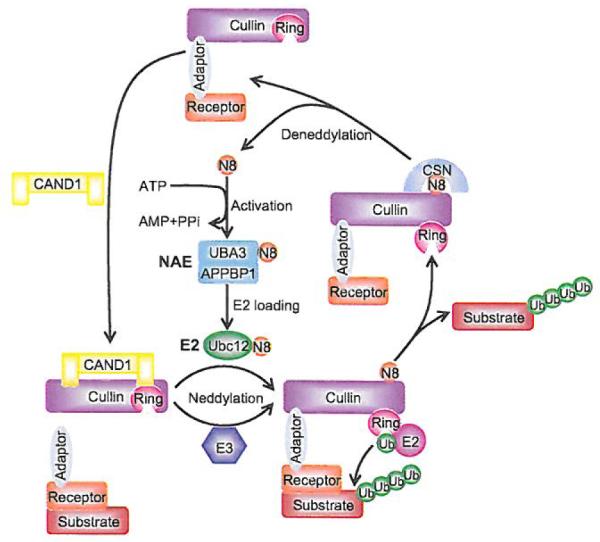
The binding of unmodified cullin to CAND1 inhibits the binding of the substrate receptor-adaptor module to the N-terminus of cullin. Neddylation of cullin disrupts the inhibitory binding by CAND1 and retains the CRLs in an active conformation to promote substrate ubiquitination. Like ubiquitination, neddylation requires E1 NEDDS-activating enzyme (NAE), E2 NEDD8-conjugating enzyme (UBC12), and E3 NEDD8 ligase, which catalyzes the transfer of NEDD8 to cullin. After dissociation of polyubiquitinated substrate from CRL complex, CSN binds to neddylation site of cullin and removes NEDD8 from cullin for recycle. CAND1 then binds to cullin and inactivates the CRLs.
