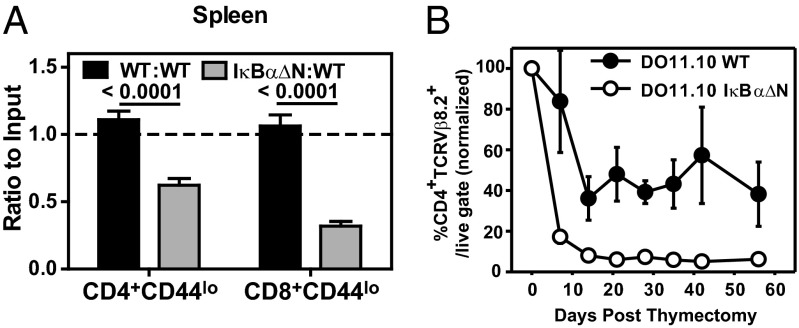
Fig. 2.
Basal NF-κB is required for T-cell survival in vivo. (A) Equal numbers of CD45.1/2 WT and CD45.2 WT or IκBα∆N CD4+CD44lo and CD8+CD44lo cells were coadoptively transferred into CD45.1 recipients. Seven days later, ratios of IκBαΔN:WT and WT:WT splenic CD4+CD44lo and CD8+CD44lo T cells were assessed as follows: (% CD45.2final/% CD45.1/2final)/(% CD45.2initial/% CD45.1/2initial). The graph represents recipients receiving WT:WT (n = 13) and IκBαΔN:WT (n = 14) cells. Data are pooled from five independent experiments and analyzed by Kruskal–Wallis test with Dunn’s posttest. (B) DO11.10/WT and DO11.10/IκBα∆N mice were thymectomized, and presence of CD4+TCRVβ8.2+ T cells in peripheral blood was assessed weekly by flow cytometry (WT, n = 6; IκΒαΔN, n = 8). Values displayed are percentages of CD4+TCRVβ8.2+ T cells with respect to the live gate and relative to the value obtained at the time of thymectomy (day 0). Data are representative of two independent experiments.