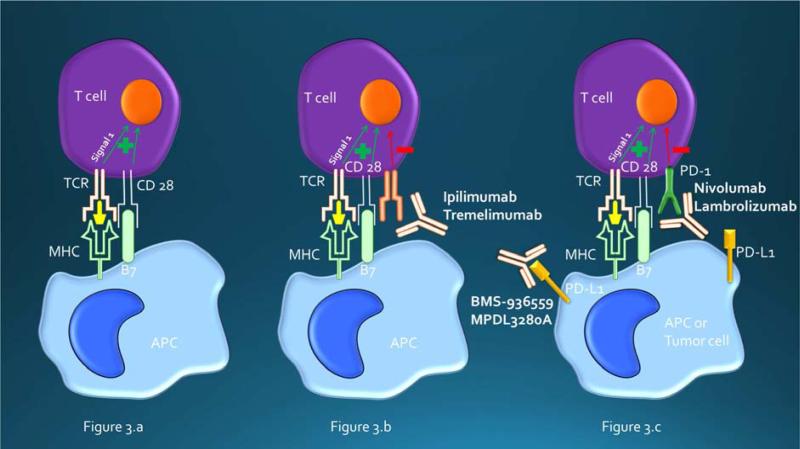
Figure 3.
Figure 3.a. T-cell activation with positive co-stimulation.
Figure 3.b. CTLA-4 is a negative regulator of T-cell activation. CTLA-4 inhibitors binds to CTLA-4 and blocks the interaction of CTLA-4 with its ligand, B7. Blockade of CTLA-4 augments T-cell activation and proliferation.
Figure 3.c. Engagement of PD-1 expressed on T cells with PDL-1 expressed on APC or tumor cells results in T-cell suppression and tumor protection. Blockade of this interaction with either PD-1 or PDL-1 blocking antibodies can “wake up” exhausted T cells, resulting in a T-cell response against tumor. APC = antigen-presenting cell; CTLA-4 = cytotoxic T-lymphocyte antigen-4; MHC = major histocompatibility complex; PD-1 = programmed death 1; PDL-1 = programmed death ligand-1; TCR = T-cell receptor