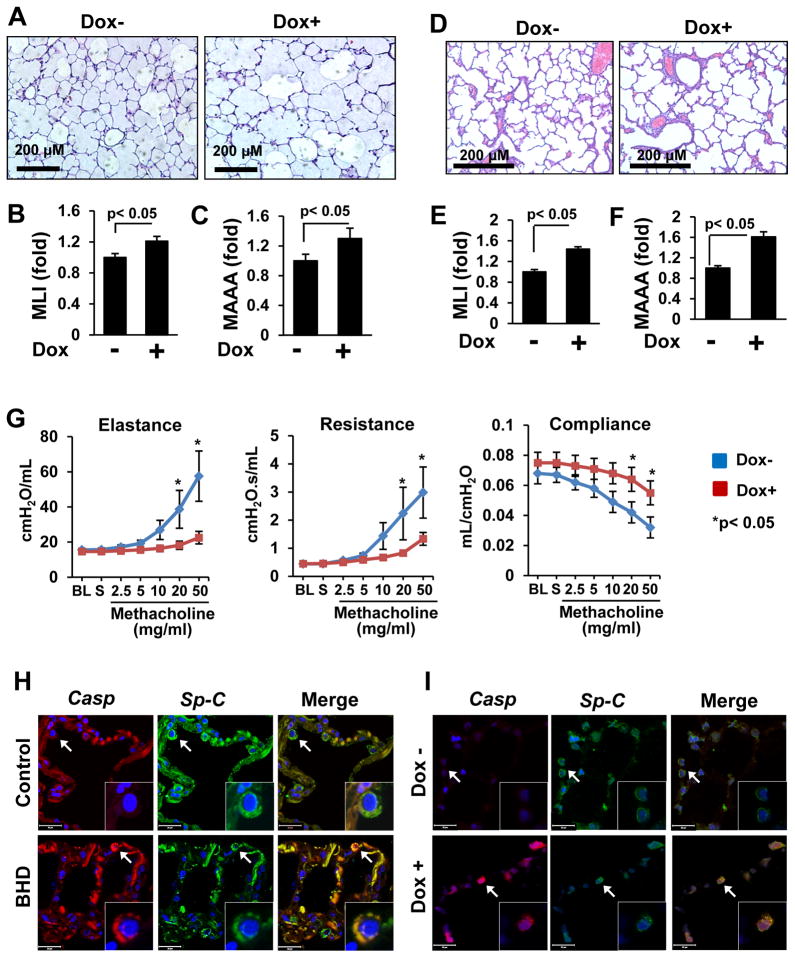
Figure 2. Loss of FLCN increases pulmonary alveoli, impairs lung function and induces alveolar epithelial cell apoptosis.
(A–C) Flcn loss results in alveolar enlargement in Flcnf/f:SP-C-Cre mice treated as in (1D). Scale bars, 200 μM.
(D–F) Enlarged alveoli in pups with FLCN deletion in lung epithelium. Scale bars, 200 μM.
(G) FLCN deletion in Flcnf/f:SP-C-Cre mice impairs lung function, n=8 per group. BL–baseline; S-saline.
The mean is shown; error bars represent SE (n>3). Data for Dox- mice are taken as one fold.
(H) Cleaved caspase-3-positive (red) cells in lung epithelium (SP-C, green) of BHD lung, (n=5) but not in control (n=3) lung.
(I) Loss of Flcn in lung epithelium (SP-C, green) results in alveolar epithelial cell apoptosis (red) in lung from Flcnf/f:SP-C-Cre mice treated as in (1D), n=3 per group.
Scale bars, 20 μM.
See also Figure S2.