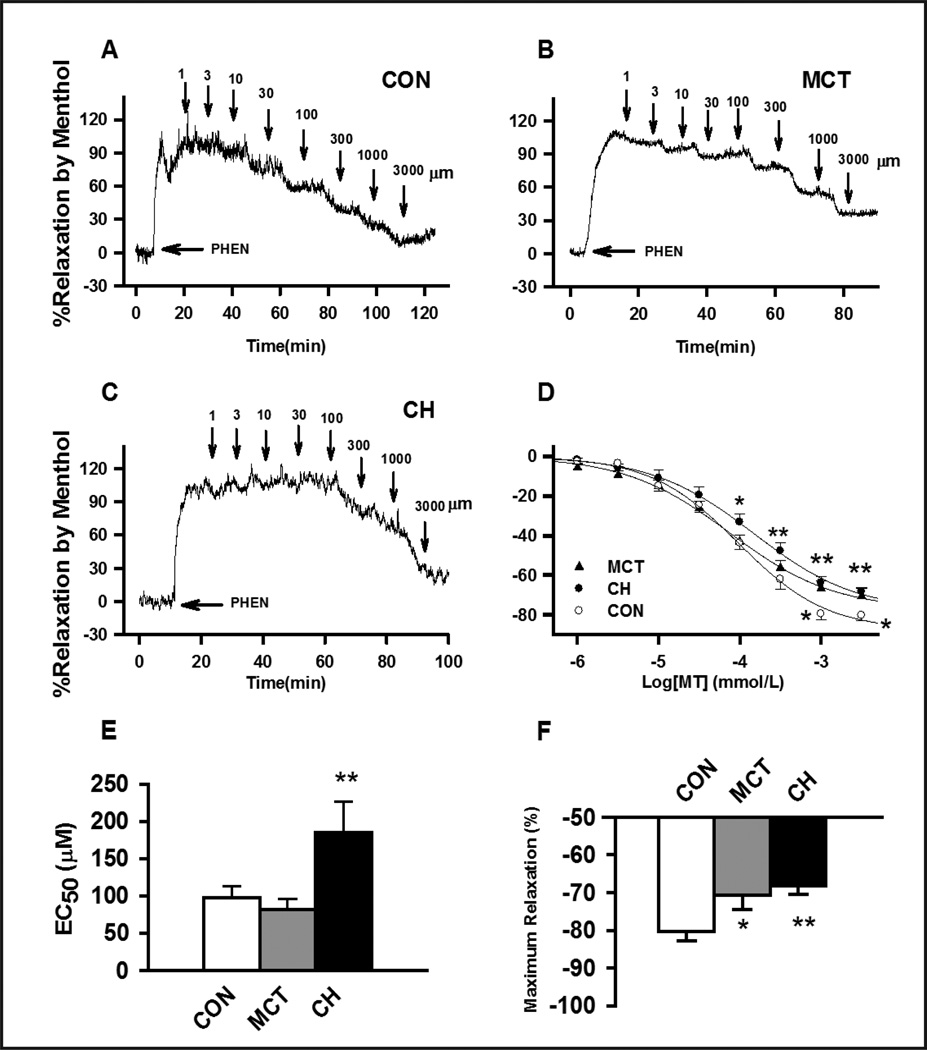
Fig. 5. Menthol-induced the concentration-dependent inhibition of 1μM phenylephrine (PHEN) pre-contracted de-endothelialized PAs in control, MCT- and CH- treated rats.
(A), (B) and (C) representative concentration-dependent relaxation traces caused by menthol on 1μM PHEN pre-contracted PAs in control, MCT and CH rats, respectively. Tension is expressed as a percentage of the contractile response induced by 60mM KCl. (D) Average percent inhibition of PHEN-induced contractions caused by various concentrations of menthol in PAs of control, MCT and CH rats. (E) and (F) are the averaged EC50 and averaged maximum percent inhibition of PHEN-induced contractions caused by menthol. Arrows indicate the application of menthol at various concentrations. 13 to 14 experiments from at least 3 different animals were performed for each group, * indicates P<0.05, and ** indicates P<0.01 comparing to the control group.