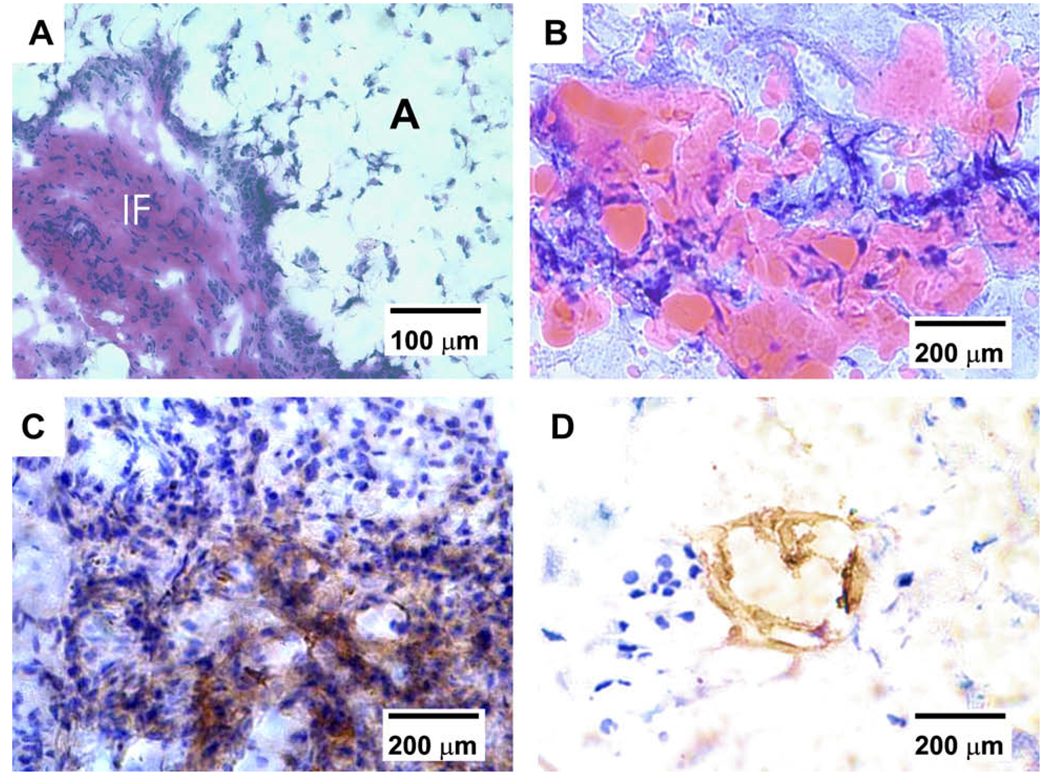
Fig. 3.
Histological and immunohistochemical characterization of vascularized adipose tissue from human mesenchymal stem cells. (A) Hematoxylin and eosin staining revealed IF tissue interposing between foam-like space labeled with A for adipose tissue. The presence of adipose tissue is confirmed in (B), showing substantial Oil red O positive staining in PEG hydrogel encapsulating hMSC-derived adipogenic cells, in addition to bFGF and built-in microchannels. In contrast, there is no evidence of adipogenesis in PEG hydrogel with bFGF and built-in microchannels, despite the seeding of hMSCs but without adipogenic differentiation. (C) Positive immunolocalization of VEGF antibody in the IF tissue interposing areas of adipogenesis, indicating the presence of vascular supply. (D) Positive immunolocalization of lectin WGA in the interstitial fibrous tissue interposing areas of adipogenesis, serving as further indication of the presence of vascular endothelial cells.