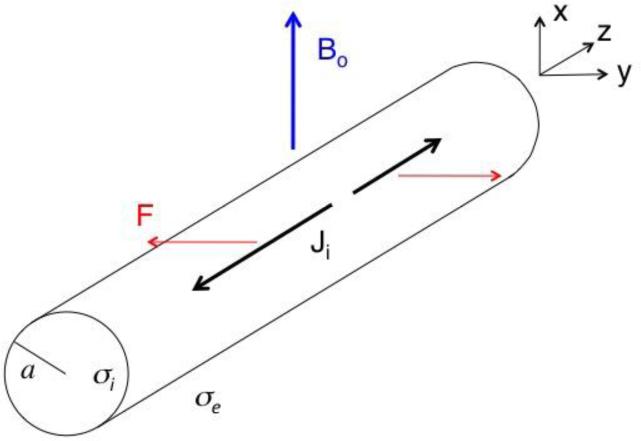
Figure 1.
A schematic diagram of a nerve of radius a carrying action current Ji (black, thick arrows) along the z axis in a static magnetic field (blue, thick arrow) of strength Bo oriented perpendicular to the axon (the x direction). The Lorentz force F (red, thin arrows) causes the nerve to move in the y direction. The intracellular conductivity is σi, and the extracellular conductivity is σe.