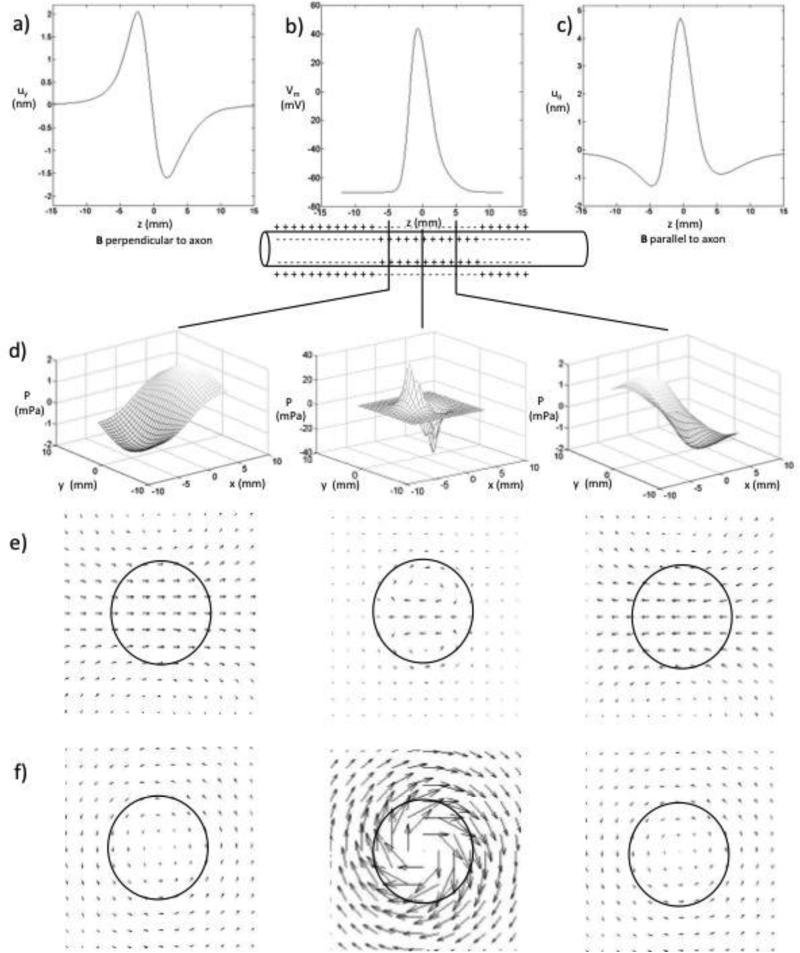
Figure 3.
a) The displacement in the y direction, calculated at r=0, for the magnetic field perpendicular to the nerve. b) The transmembrane potential as a function of z. c) The displacement in the direction, calculated at r=a, for the magnetic field parallel to the nerve. d) The pressure as a function of x and y for three axial locations: z = -5, 0, and 5 mm, for the magnetic field perpendicular to the nerve. When the magnetic field is parallel to the nerve, the pressure vanishes. e) The displacement for the magnetic field perpendicular to the nerve (x is vertical, y is horizontal) ), at z = -5, 0, and 5 mm. f) The displacement for the magnetic field parallel to the nerve), at z = -5, 0, and 5 mm.