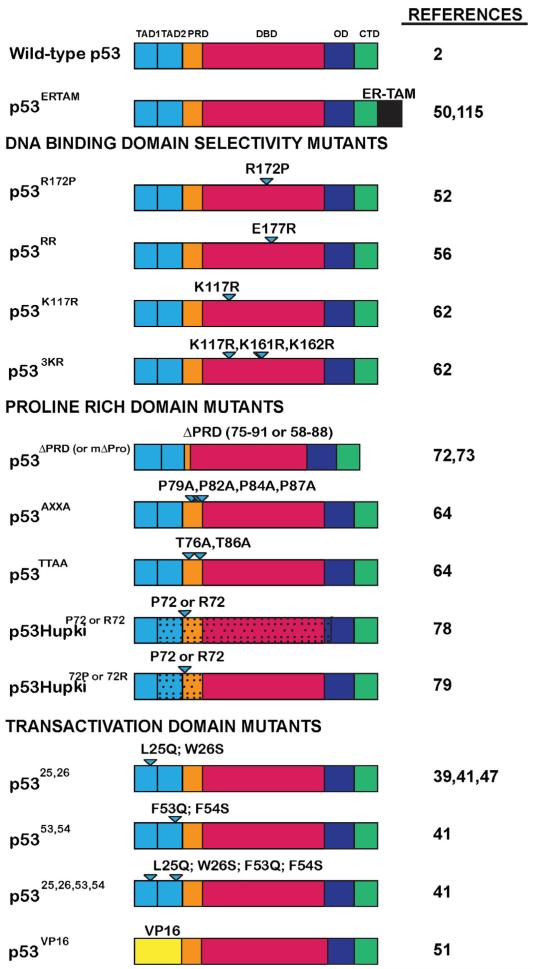
Fig. 2.
p53 domain mutants investigated in knock-in mouse models. The p53 domain mutants described in this review are categorized according to the functional domains targeted. Wild-type p53 is shown for reference. p53 functional domains: TAD1 = transactivation domain 1; TAD2 = transactivation domain 2; PRD = proline rich domain; DBD = DNA-binding domain; OD = oligomerization domain; CTD = C-terminal domain. Triangles denote mutated amino acids. ERTAM = tamoxifen-inducible estrogen receptor ligand-binding domain; VP16-herpes simplex viral protein 16 transactivation domain. RR is so-called because of the E180R mutation adjacent to the unmutated residue R181. Even though it is a tumor-derived mutant, p53R172P is listed here again because it has been used for structure–function analysis of p53. Stippling indicates regions of p53 replaced with human sequences in the HUPKI mouse models.