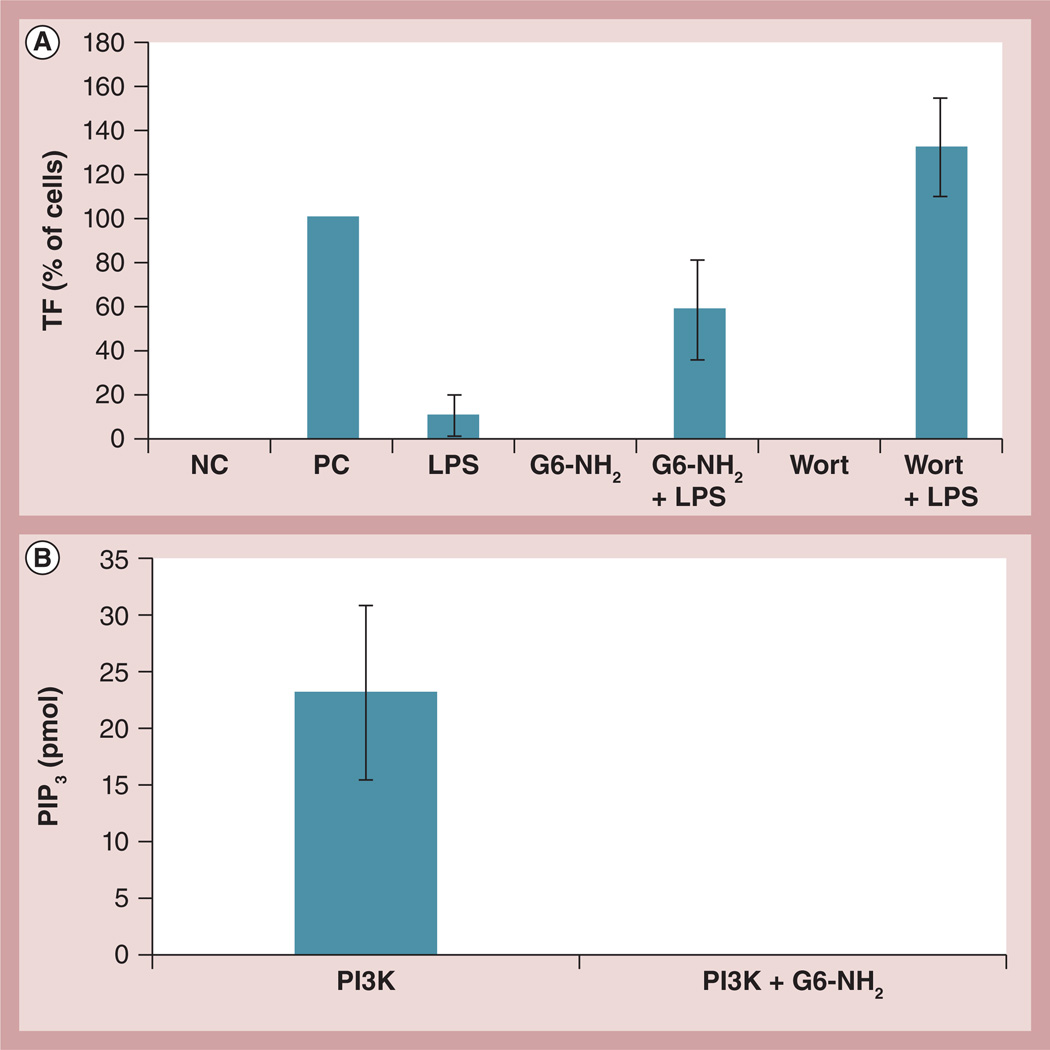
Figure 7. Probing the role of phosphoinositol 3 kinase in the enhancement of lipopolysaccharide-induced procoagulant activity by cationic dendrimers.
(A) Peripheral blood mononuclear cells from healthy donor volunteers were treated for 24 h with 1 ng/ml of LPS, 4 µg/ml of G6-NH2, or the combination (LPS + G6-NH2). Cells were also treated with 100 nM Wort alone or in combination with LPS (Wort + LPS). Tissue factor expression on monocyte surfaces was measured by flow cytometry. Shown is the mean percentage of positive cells relative to the positive control. Media was used as the NC and 10 µg/ml of LPS was used as the PC. (B) Recombinant human PI3K was immunoprecipitated with anti-p85 antibody followed by several washes; the beads with isolated PI3K were then incubated with 12.5 µg/ml G6-NH2. After eight washes to remove excess dendrimer, the kinase activity was assessed by incubation with phosphatidylinositol (4,5)-biphosphate substrate. Shown is the mean amount of PIP3 generated from the kinase reaction ± standard deviation (n = 3).
G6-NH2: Generation 6 amine-terminated polyamidoamine dendrimer; LPS: Lipopolysaccharide; NC: Negative control; PC: Positive control; PI3K: Phosphoinositol 3 kinase; PIP3: Phosphatidylinositol (3,4,5)-triphosphate; Wort: Wortmannin.