Figure 8.
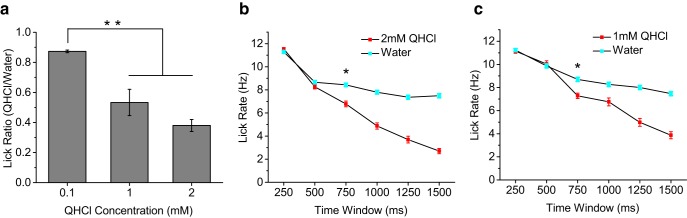
Brief-access test reveals that mice require ∼500–750 ms to detect bitter. a, Comparison of quinine/water lick ratios during 3 s brief-access testing for increasing concentrations of quinine (mean ± SEM). Mice significantly reduced licking to both 1 and 2 mm quinine compared with 0.1 mm quinine, indicating that they could detect these concentrations of quinine that were used in the stop-signal task (p < 0.01, ANOVA). b, c, Lick-rate comparisons for water and quinine stimuli using nonoverlapping 250 ms time windows. Data are plotted as mean ± SEM. Mice did not begin to significantly change lick rate (denoted by asterisk) to quinine until 500–750 ms after stimulus contact (p < 0.00001, t test).
