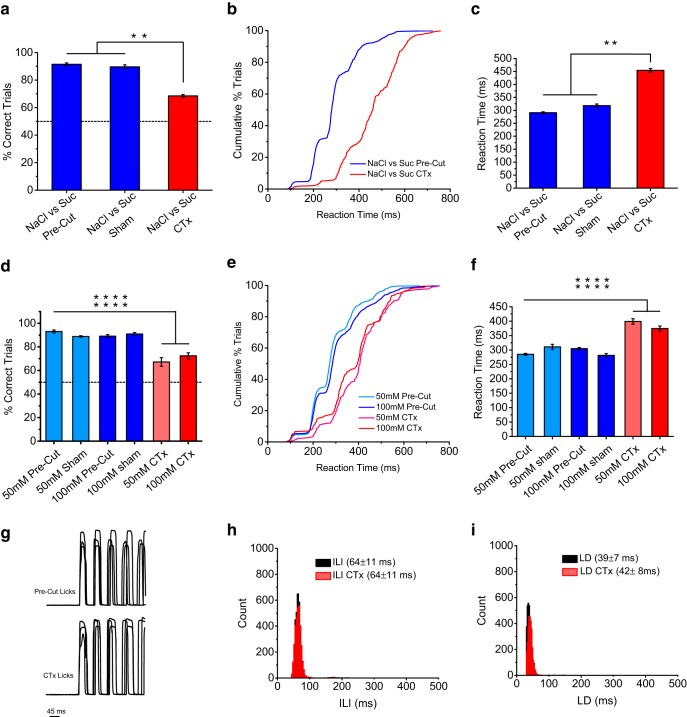
Figure 9.
CTx reduces the speed of salt perception. a, Performance discriminating NaCl from sucrose before and after CTx. Data plotted as mean ± SEM. Mice showed a significant drop in performance accuracy after CTx (p < 0.0001 ANOVA). Stimuli were 100 and 50 mm NaCl and 300 and 100 mm sucrose. b, c, Cumulative distributions and average reaction times for mice discriminating NaCl from sucrose before and after CTx. Mice showed a significant reduction in their speed of accurate discrimination after CTx (p < 0.00001, ANOVA). Results in c are plotted as mean ± SEM. d–f, Similar results were found for the NaCl detection version of stop-signal task after CTx, with mice showing a significant reduction in speed of NaCl detection at all concentrations tested. Asterisks denote significant change for each individual comparison (p < 0.0001, ANOVA). g–i, Measurements of LD and ILI for before and after CTx showed little change (note overlap in distributions). We observed only small changes in LDs, with no changes in ILIs. Overall, the results demonstrate that the effect on speed of NaCl identification after CTx was sensory in origin and not motor.