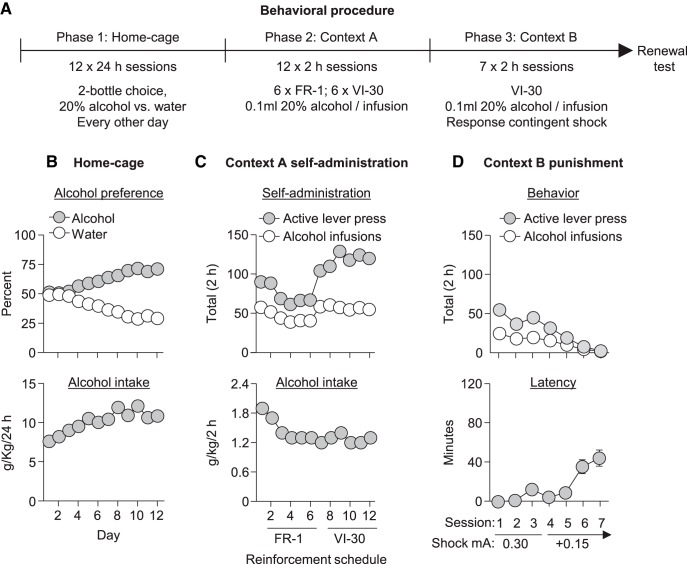
Figure 1.
Home-cage intake, initial alcohol self-administration in context A, and subsequent alcohol self-administration in context B (punishment). A, Outline of the experimental procedure before test. B, Mean ± SEM preference for 20% alcohol or water and alcohol intake (grams per kilogram) during the home-cage access to 20% alcohol. The SEMs for these data points are smaller than the symbol size. C, Mean active lever presses and alcohol deliveries and alcohol intake during the alcohol self-administration training in context A (6 sessions with each reinforcement schedule). D, Mean active lever presses, alcohol deliveries, and latency to the first lever press during punishment in context B. After the third session, rats with >15 active lever presses in the 2 h session were given additional sessions with increased shock intensity. Data are from all rats in Experiments 1–3; total n = 69.